Fig. 2.
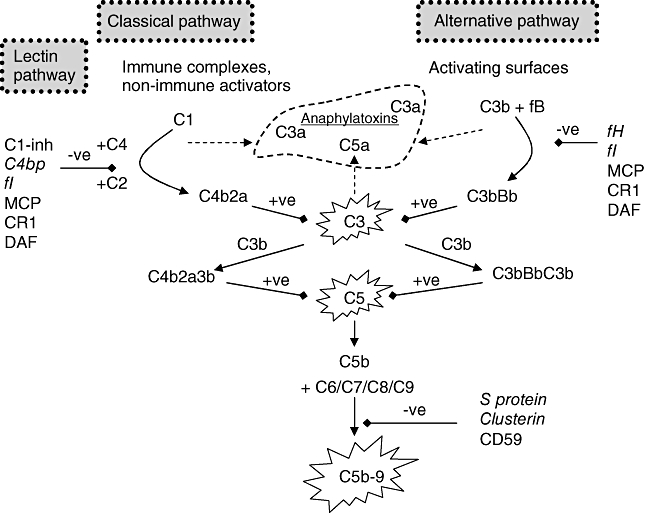
Activation and regulation of the complement (C) system: activation through both classical and alternative pathways results in the formation of C5 convertases, cleaving C5 and eventually forming the membrane attack complex (C5b–9). They also result in the formation of anaphylatoxins which cause inflammation and chemotaxis. The C system is under tight regulation by soluble (in italics) and membrane-bound (in bold) proteins (C1-inh, C1 inhibitor; C4bp, C4 binding protein; fI, factor I; MCP, membrane co-factor protein; CR1, C receptor 1; DAF, decay accelerating factor; fH, factor H; fB, factor B).
