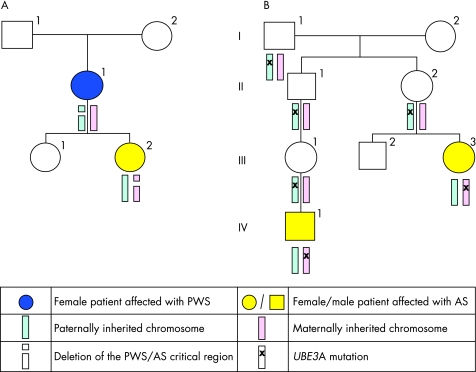
Figure 2 Pedigrees illustrating the inheritance of Prader–Willi and Angelman's syndromes (PWS/AS). (A) Pedigree showing individual II:1 with a de novo deletion of the PWS/AS critical region on 15q11‐q12 on her paternal allele, resulting in Prader–Willi syndrome. One of her daughters, III:2, has inherited this deletion and has Angelman's syndrome (as the deletion is on her maternal allele). (B) Pedigree showing two individuals, III:3 and IV:1, with Angelman's syndrome due to a UBE3A mutation. The mutation only manifests if it passed through a female carrier (II:2 and III:1). Individuals I:1, II:1, II:2 and III:1 have all inherited the UBE3A mutation from their fathers. Their paternally derived chromosome is imprinted (naturally switched off) so they are phenotypically normal. III:2 has inherited the maternally derived chromosome without the UBE3A mutation.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.