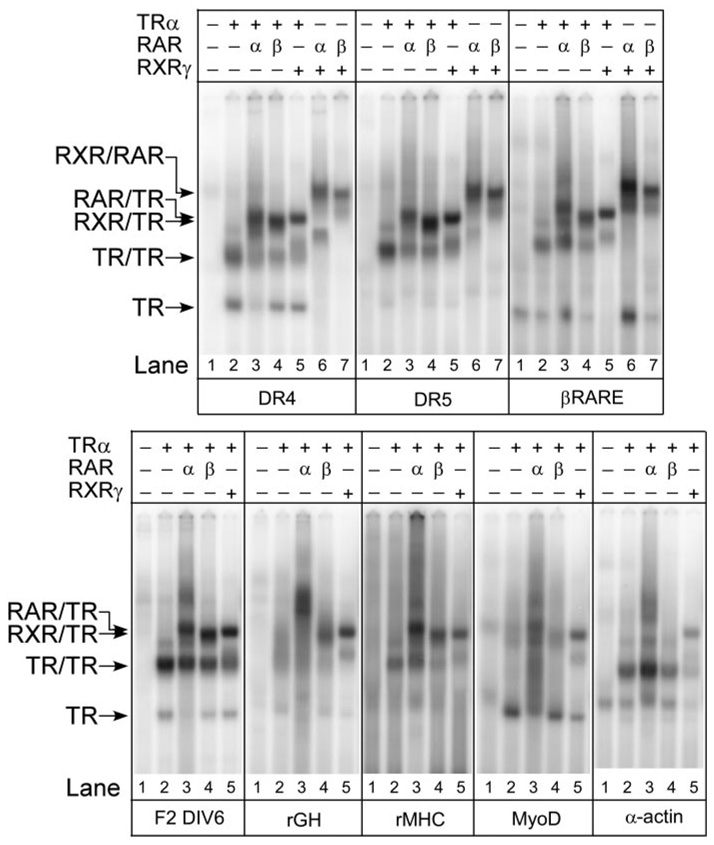
Fig. 5. RAR/TR Heterodimers Bind to Natural DNA Response Elements.
TRα, RARα, RARβ, and RXRγ proteins were tested for the ability to bind to different natural and synthetic DNA elements using an EMSA protocol as in Fig. 1. TRα, RARα, and RXRγ were used at approximately 40 ng, 20 ng, and 11 ng per assay, respectively; RARβ was titrated to yield equal homodimer formation as RARα. Radiolabeled DNA probes included a consensus DR-4, a consensus DR-5, the retinoid response element in the RARβ promoter (β-RARE), or the T3-response elements found in the F2-lysozyme promoter (F2-DIV-6), rGH promoter, rMHC promoter, human MyoD promoter, and α-actin promoter. For each probe, receptor preparations were tested individually or in combination as indicated above each panel. The positions of receptor/DNA complexes representing TR monomers, TR homodimers, RAR/TR heterodimers, RXR/TR heterodimers, and RXR/RAR heterodimers are indicated to the left of the panels. Comparable results were obtained in repeated studies; a representative experiment is presented. No hormone was used in these assays.