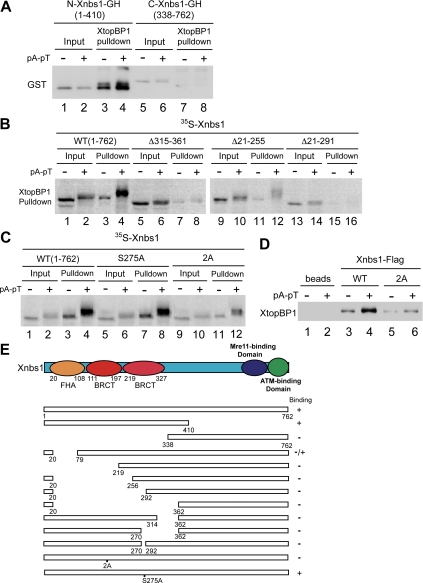
Figure 3.
The tandem BRCT domains of Xnbs1 are required for interaction with XtopBP1. (A) Recombinant HF-XtopBP1 on anti-FLAG antibody beads was incubated in egg extracts containing N-terminal (lanes 3 and 4) or C-terminal fragments of Xnbs1 (lanes 7 and 8) in the absence or presence of pA-pT. Beads were reisolated and immunoblotted for GST. Lanes 1, 2, 5, and 6, initial extract aliquots. (B) 35S-Labeled versions of full-length Xnbs1 (WT) (lanes 1–4) and the Δ315–361, Δ21–255, and Δ21–291 deletion mutants of Xnbs1 (lanes 5–16) were incubated in egg extracts containing HF-XtopBP1 bound to anti-FLAG antibody beads in the absence or presence of pA-pT. The beads were isolated, and bound 35S-labeled proteins were detected by SDS-PAGE and phosphorimaging (lanes 3, 4, 7, 8, 11, 12, 15, and 16). Lanes 1, 2, 5, 6, 9, 10, 13, and 14, initial extract aliquots. (C) 35S-Labeled versions of wild-type, S257A, and 2A Xnbs1 were analyzed for binding to XtopBP1 as described in B. (D) Wild-type and 2A mutant versions of Xnbs1-FLAG on anti-FLAG antibody beads were incubated in egg extracts lacking or containing pA-pT. Beads were reisolated and immunoblotted for XtopBP1. (E) Summary of the abilities of the indicated forms of Xnbs1 to interact with XtopBP1.