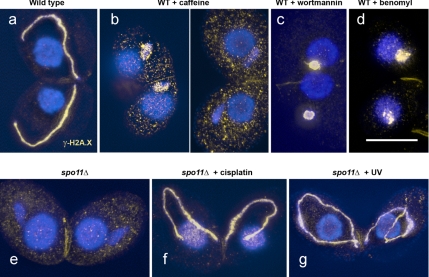
Figure 5.
Induction of γ-H2A.X signals in meiotic MICs. In wild type, strong γ-H2A.X immunostaining (orange) is detected in elongated MICs (a). After treatment with caffeine, H2A.X phosphorylation is partially suppressed (two examples with different intensities of γ-H2A.X labeling shown in panel b, whereas upon wortmannin treatment labeling is always strong (c). Also after benomyl (d) and nocodazole (not shown) treatment, γ-H2A.X signals are found, suggesting that other aspects of meiosis progress despite the failure of MICs to elongate. In the spo11Δ mutant, γ-H2A.X labeling is not observed (e). Cisplatin restores strong γ-H2A.X labeling in the mutant (f). Also UV-radiation induces γ-H2A.X foci in the mutant (g), but they become fewer and disappear ca. 90 min after the treatment. Bar, 10 μm.