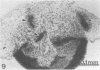
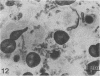
Abstract
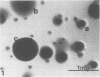
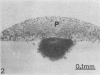
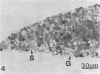
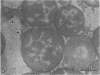
Staphylococcus aureus strains of bovine origin were induced to L-form by exposure to 100 U of penicillin in brain heart infusion broth supplemented with 5% NaCl, 5% sucrose, and 10% horse serum. L-forms were cultured on similarly supplemented brain heart infusion agar containing no antibiotic. Light and electron microscopic examination of plastic-embedded L-form colonies revealed a variety of morphologic types. The primary site of growth appeared to be the core area below the agar surface, consisting mainly of pleomorphic budding forms. At the surface, these forms gave rise to large spherules with a gradation from smaller to larger spherules toward the periphery of the colony. Some colonies progressed to reverting forms with the growth of bacterial cells containing cell wall. In addition to L-forms, intermediate colony forms were observed that lacked typical L-form morphology and progressed rapidly to the parent cell form on subculture to bovine blood agar. Description of these forms will be used in the search for similar morphologic types in vivo during antibiotic treatment of chronic S. aureus bovine mastitis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DIENES L., SHARP J. T. The role of high electrolyte concentration in the production and growth of L forms of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1956 Feb;71(2):208–213. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.2.208-213.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIENES L., WEINBERGER H. J., MADOFF S. The transformation of typhoid bacilli into L forms under various conditions. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jun;59(6):755–764. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.6.755-764.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienes L., Bullivant S. Morphology and reproductive processes of the L forms of bacteria. II. Comparative study of L forms and Mycoplasma with the electron microscope. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):672–687. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.672-687.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienes L. The Isolation of L Type Cultures from Bacteroides with the Aid of Penicillin and Their Reversion into the Usual Bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1948 Oct;56(4):445–456. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.4.445-456.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J. Morphology and ultrastructure of staphylococcal L colonies: light, scanning, and transmission electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):1049–1053. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.1049-1053.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. T., Heidger P. M., Jr, Domingue G. Proposed reproductive cycle for a relatively stable L-phase variant of Streptococcus faecalis. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):915–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.915-927.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato Y., Hirachi Y., Toda Y., Takemasa N., Kotani S. Effect of the composition of reversion medium on change of Staphylococcus aureus lysostaphin protoplasts to coccal forms and L-forms. Biken J. 1986 Jun;29(2):39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landman O. E., Ryter A., Fréhel C. Gelatin-induced reversion of protoplasts of Bacillus subtilis to the bacillary form: electron-microscopic and physical study. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2154–2170. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2154-2170.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki N., Akema R., Miyamoto Y. Difference in L-form inductivity of various serotypes of group A streptococci. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(4):403–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens W. E. Evaluation of various antibiotics for induction of L forms from Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from bovine mastitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2187–2190. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2187-2190.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens W. E. Isolation of Staphylococcus aureus L forms from experimentally induced bovine mastitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1956–1961. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1956-1961.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönfeld J. K., de Bruijn W. C. Ultrastructure of the intermediate stages in the reverting L-phase organisms of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus faecalis. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Aug;77(2):261–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-77-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears P. M., Fettinger M., Marsh-Salin J. Isolation of L-form variants after antibiotic treatment in Staphylococcus aureus bovine mastitis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1987 Sep 15;191(6):681–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]