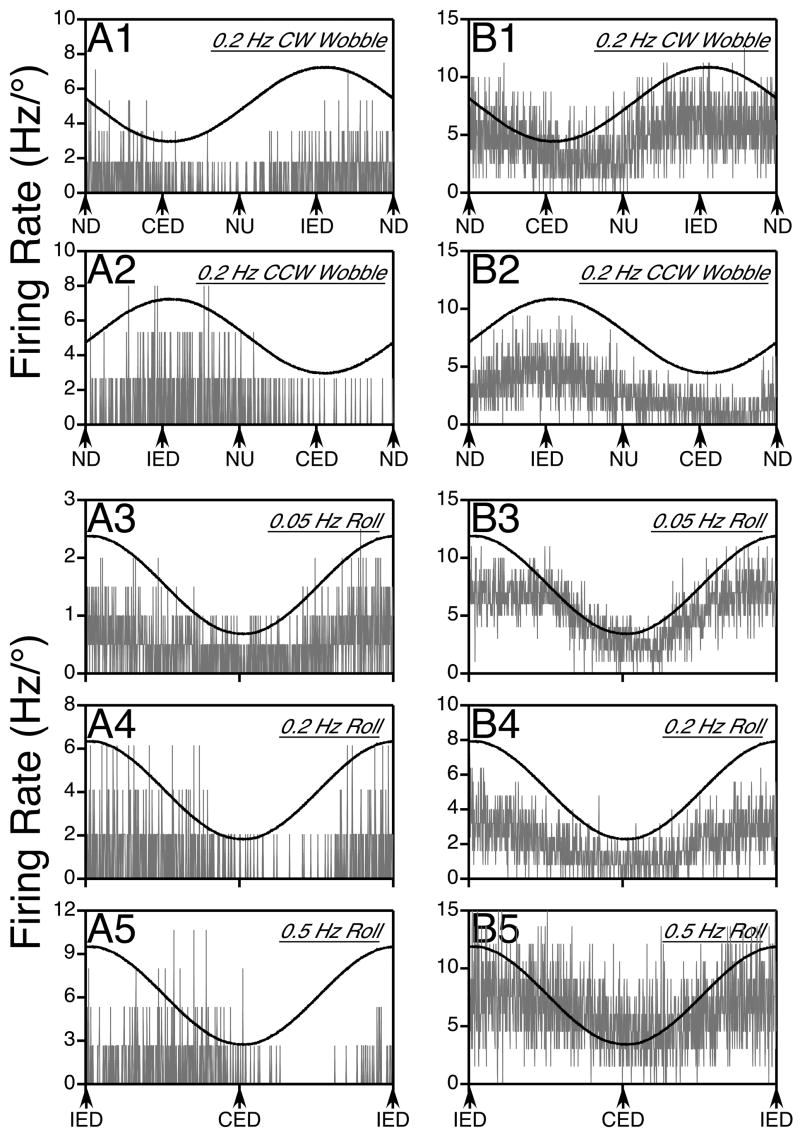
Figure 4.
Responses of two putative thoracic interneurons to sinusoidal rotations in vertical planes; gray traces show average neuronal firing rate (in Hz per degree of rotation), whereas black traces indicate the position of the tilt table. Column A illustrates data for a neuron whose responses lagged stimulus position as rotational frequency was increased, whereas column B provides data for a cell with responses in phase with tilt position. In each column, traces 1 and 2 respectively show the responses to 0.2 Hz CW and CCW wobble stimuli, whereas traces 3–5 depict the responses to 0.05 Hz (trace 3), 0.2 Hz (trace 4), and 0.5 Hz (trace 5) roll rotations. The responses illustrated in panels A1, A2, A4, and A5 were elicited by 7.5° rotations, whereas the others were produced by 10° tilts. Approximately 15 sweeps were averaged when wobble stimuli were delivered (traces A1, A2, B1, B2), whereas the following number of sweeps were averaged during roll tilts: 9 for trace A3, 13 for A4, 24 for A5, 5 for B3, 20 for B4, and 33 for B5. Abbreviations: CED, contralateral ear-down roll; CW, clockwise; CCW, counterclockwise; IED, ipsilateral ear-down roll, ND, nose-down pitch, NU, nose-up pitch.