FIG. 3.
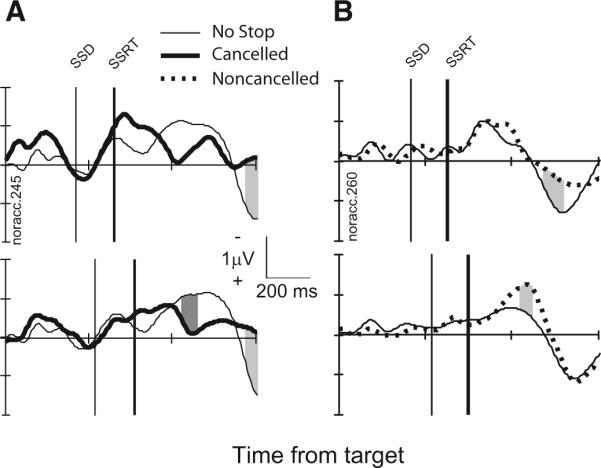
LFP in stop signal trials from a representative site. A: comparison of LFP in cancelled stop signal trials (thick) and latency-matched no-stop signal trials (thin) with stop signal delays of 169 ms (top, 198 no-stop trials trials; 26 cancelled trials) and 217 ms (bottom, 137 no-stop trials; 58 cancelled trials). Intervals in stop signal trials in which polarity is significantly more negative are highlighted by dark gray. Intervals in stop signal trials in which polarity is significantly more positive are highlighted by light gray. B: comparison of LFP in noncancelled stop signal trials (thick, dotted) and latency-matched no-stop signal trials (thin) with stop signal delays of 217 ms (top, 67 no-stop trials; 19 cancelled trials) and 269 ms (bottom, 165 no-stop trials; 49 cancelled trials).
