Figure 8.
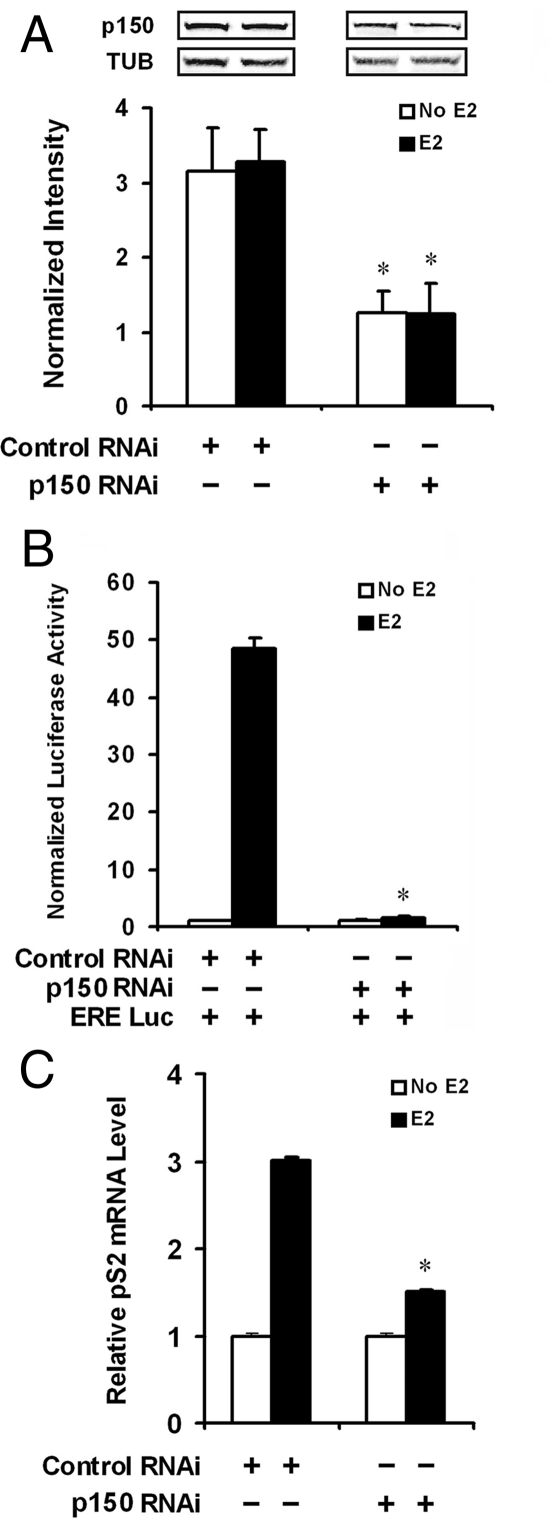
p150/glued is required for full activation of estrogen-dependent gene expression in MCF-7 cells. We designed RNAi oligonucleotides against human p150/glued (see Materials and Methods), which were transfected into MCF-7 cells. A, Western analysis demonstrated that compared with control RNAi, there was approximately 50% inhibition of p150/tubulin (TUB) protein levels when pair 56 p150-specific RNAi was used (normalized to loading controls). Bands are from the same Western blot of one representative experiment. B, We compared estrogen-stimulated ERE-luciferase expression in MCF-7 cells cotransfected with RNAi (pair 56) 48 h after transfection. As before, Renilla luciferase cotransfection was performed in all groups to normalize transfection efficiencies. This experiment demonstrated a significant decrease in the potency of estrogen-stimulated transcription when p150/glued protein levels were inhibited. Statistical analyses were performed to compare groups with and without p150/glued RNAi; asterisk denotes a significant reduction in estrogen-stimulated luciferase activity with p150 RNAi compared with control RNAi (P < 0.05). C, Inhibition of p150 expression by RNAi impairs endogenous pS2 gene expression. MCF-7 cells were transfected with p150 or control RNAi and treated with estrogen to stimulate endogenous ERα-dependent transcription. Relative pS2 mRNA, measured by quantitative PCR, was significantly suppressed after p150 RNAi treatment. *, Significant reduction in estrogen-stimulated mRNA levels with p150 RNAi compared with control RNAi (P < 0.05).