FIGURE 3.
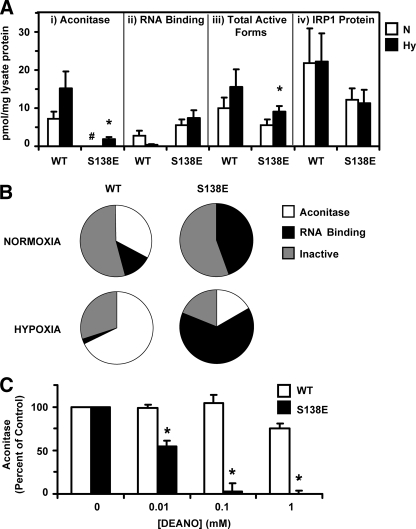
Effect of hypoxia on aconitase and RNA binding activity of IRP1WT and IRP1S138E expressed in HEK 293 cells. A, calculated distribution of aconitase and RNA-binding forms for WT (n = 3) and S138E (n = 4) in cells grown under normoxic (N) or hypoxic (Hy) conditions. The activities and protein levels are for the tet-induced IRP1; endogenous (–tet) aconitase activities or protein levels have been subtracted. RNA binding was determined using antibody supershift EMSA with the anti-Myc antibody. The mass of the c-acon pool was determined using the established specific activity of purified c-acon, and the mass of the RNA binding pool was determined by using the specific radioactivity of the [32P]RNA used for EMSA and assumed a 1:1 IRP1/IRE ratio under saturating conditions (see “Experimental Procedures”). Panel i, aconitase activity attributable to IRP1WT or IRP1S138E was determined. For normoxic S138E lysate acon activity, the resulting value was below zero, denoted by #. Panel ii, effect of hypoxia on RNA binding activity of IRP1WT and IRP1S138E was also determined. Although the mean RNA binding appeared to decrease for IRP1WT in hypoxia, the difference was not statistically significant. The mean RNA binding activity of IRP1S138E was not reduced by hypoxia. Panel iii, total active forms of IRP1/c-acon was determined by summing the aconitase and RNA binding activity for the wild type and S138E phosphomutant under each condition using the data in Panels i and ii. Panel iv, IRP1 protein was quantified in lysates by anti-IRP1 immunoblot using purified recombinant IRP1 for the standard curve. An asterisk indicates hypoxia value significantly different from corresponding normoxia control (Student's t test, p ≤ 0.05). B, pie chart representation of the data in A. The percentages of forms were calculated by dividing the active form (pmol/mg lysate protein) by the total IRP1 protein (pmol/mg lysate protein) from the quantitative immunoblot. When activity was below the endogenous background, which occurred only for acon activity of S138E lysates in normoxia, a value of zero percent was assigned. C, freshly prepared lysates from HEK cells were anaerobically treated with DEANO or an equivalent volume of carrier buffer (control). After a 15-min incubation each reaction was quenched in assay mix (0.1 m Tris, pH 8.0, 20 mm dl-isocitrate), and aconitase activity was measured. Endogenous activity (–tet) was subtracted from total activity (+tet) to determine the activity caused by c-acon encoded by the transgene. Starting aconitase activity for c-aconWT was 40.3 ± 12.4 millinunits/mg protein, whereas for c-aconS138E it was 8.7 ± 1.8 milliunits/mg protein (means ± S.E., n = 3). An asterisk denotes c-aconS138E activity significantly lower than corresponding c-aconWT activity (Student's t test, two-tailed, unpaired, n = 3, p < 0.05). WT, wild type.