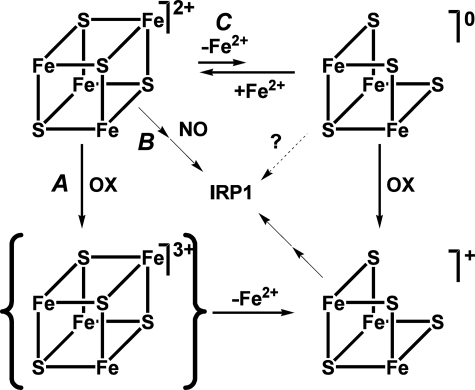
FIGURE 5.
A model for pathways of cluster disassembly in phosphorylated c-acon. In Ser138-phosphorylated c-acon the [4Fe-4S]2+ cluster can undergo oxidative (A) or NO-induced (B) disassembly as its nonphosphorylated counterpart does or lose Fea prior to oxidation (C). OX stands for oxidant. Although the loss of Fea is shown as a reversible process, the instability of the [3Fe-4S]0 cluster and the possible interaction of Fe2+ with other solutes are likely to render the process irreversible in the presence of reactive species, coordinating buffers, or chelators.