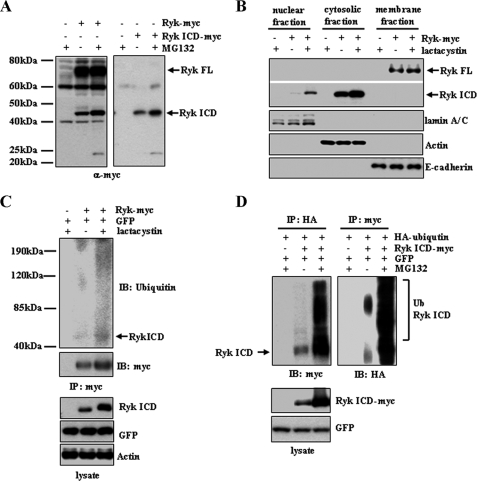
FIGURE 1.
Proteasomal degradation of the Ryk ICD. A, treatment with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 increases Ryk ICD protein levels. 293T cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding C-terminal Myc-tagged wild-type Ryk or an empty control vector. MG132 was added 6 h prior to lysis, and lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with an anti-Myc antibody. A similar experiment using 293T cells transfected with a Myc-tagged Ryk ICD construct or a control vector was also performed (right panel). B, nuclear localization of the Ryk ICD increases in cells treated with the proteasome inhibitor lactacystin. Nuclear, cytosolic, and membrane extracts of cells transfected with Ryk constructs or control plasmids were subjected to Western blotting using an anti-Myc antibody for full-length (FL) Ryk and Ryk ICD proteins. lamin A/C, actin, and E-cadherin were used as protein markers for nuclear, cytosolic, and membrane fractions, respectively. C, the Ryk ICD is ubiquitinated. Cells transfected with Ryk-Myc and GFP were treated with the proteasome inhibitor lactacystin. Cytosolic extracts were immunoprecipitated (IP) using an anti-Myc antibody and analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against ubiquitin (Ub) and Myc. Antibodies against GFP and actin served as controls. D, 293T cells were transfected with HA-ubiquitin and Ryk ICD-Myc or empty vector and then treated with MG132 for 6 h prior to lysis. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-HA or anti-Myc antibodies, followed by Western blotting (IB) using anti-Myc or anti-HA antibodies.