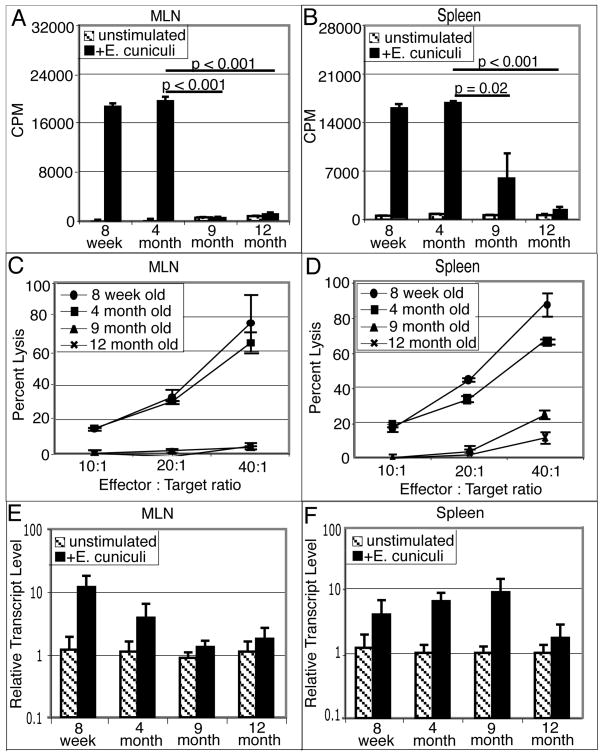
Figure 2.
Defective mucosal immune response after E. cuniculi infection. C57BL/6 mice (8 week, 4, 9 and 12 month old) were infected per-orally with 2×107 spores. Two weeks post-infection, mice were sacrificed (3 animals/group), MLN and spleen cell suspension were prepared. Proliferative response of MLN lymphocytes (A) and splenocytes (B) was measured by thymidine incorporation after 72h incubation with E. cuniculi spores. In a separate experiment, MLN (C) and spleen cell suspensions (D) were prepared and incubated with 51Cr labeled uninfected or infected macrophages at various effector to target ratios. After 4h incubation, the cytolytic activity was determined by radioisotope release into culture supernatants. MLN (E) and splenic (F) lymphocytes were isolated 14 days post E. cuniculi infection (3 mice/group). mRNA was prepared and assayed for IFNγ message by RT-PCR. Data are representative of two separate experiments.