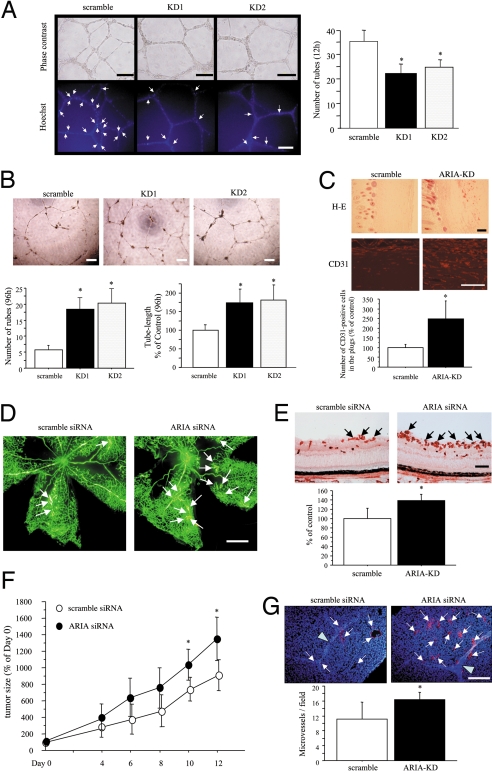
Fig. 6.
ARIA regulates angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. (A) ARIA knockdown reduced HUVEC tube formation on Matrigel at an early time point (12 h). *, P < 0.01 versus cells transfected with the scramble siRNA. Similar results were obtained in 3 independent experiments. Apoptotic cells on Matrigel were detected by Hoechst 33342 nuclear staining. Fewer apoptotic cells showing bright and condensed nuclei indicated by arrows were observed in ARIA-knocked-down HUVECs. (B) However, tube-structures were well preserved in ARIA-knocked-down HUVECs at a later time point (96 h) as compared with the control cells. *, P < 0.01 versus cells transfected with the scramble siRNA. Similar results were obtained in 2 independent experiments. (Scale bars, 200 μm.) (C) H&E staining as well as CD31 immunostaining of sections demonstrated significantly enhanced angiogenesis in the Matrigel plugs containing ARIA siRNA (ARIA-KD). (Scale bars, 100 μm.) CD31-positive endothelial cells were counted in an equal area. *, P < 0.01 versus the scramble control (n = 5 each). (D) Ischemic retinopathy was induced as described in Materials and Methods. Neovascularization (white arrows) was enhanced in retinas injected with ARIA siRNA. (Scale bar, 0.5 mm.) (E) Neovessels at the surface of retinas were detected by lectin staining (black arrows). The area of neovessels was significantly greater in the retinas injected with ARIA siRNA than in control. *, P < 0.05 versus the scramble control (n = 5 each). (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (F) Either scramble or ARIA siRNA was injected intratumorally at days 0, 4, and 8. The relative tumor volume (percentage of tumor volume on day 0) is presented in the graph. *, P < 0.05 versus tumors injected with the scramble siRNA (n = 6 each). (G) The number of CD31-positive microvessels (arrows) was significantly greater in the tumors injected with ARIA siRNA than in control. Arrowheads indicate the scars made by needle at the time of siRNA injection. *, P < 0.05 versus the scramble control (n = 6 each). (Scale bar, 100 μm.)