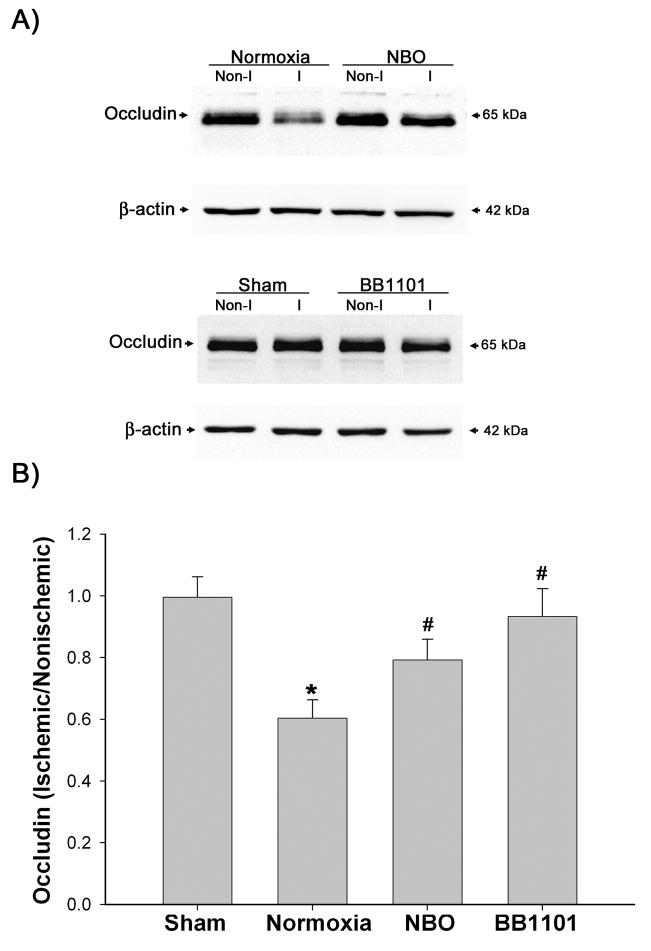
Figure 6.
The effect of NBO and MMP inhibitor BB1101 on the degradation of occludin protein in ischemic hemispheric microvessels after 90-min MCAO with 3-hr reperfusion. Cerebral microvessel lysates (10 μg) were analyzed for occludin protein by western blot. As a loading control, the blots were stripped and reprobed withβ-actin antibody. A) Representative blots of occludin and corresponding β-actin. Non-I and I represent nonischemic and ischemic hemispheric microvessels, respectively. B) The relative quantity of protein was calculated after normalization to β-actin and expressed as an occludin ratio (ischemic/nonischemic hemispheric microvessels). The occludin ratio was significantly reduced in normoxic rats (*p < 0.05 versus sham group). NBO treatment or BB1101 significantly reversed the reduction of occludin protein in ischemic hemispheric microvessels (#p < 0.05 versus normoxic group). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 4 in the sham group, n = 7 in each of the normoxic, NBO-, and BB1101-treated groups.