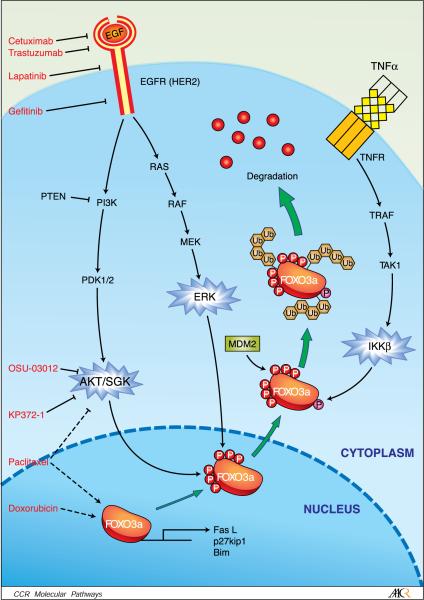
Fig. 1.
PI3K/AKT, RAS/ERK, andTNFR/IKK pathways are known to phosphorylate FOXO3a at different sites (indicated by different colors; see Table 1). Phosphorylation of FOXO3a causes FOXO3a nuclear exportation, thereby suppressing FOXO's transcriptional activity. Recently, FOXO3a phosphorylation by ERK was found to lead to FOXO3a down-regulation via MDM2-mediated proteasome degradation. Inhibition of the EGFR family that governs PI3K and RAS pathways by clinically used drugs, such as cetuximab, trastuzumab, lapatinib, and gefinitib effectively up-regulates FOXO3a. Moreover, targeting AKT/SGK byOSU-03012, paclitaxel, KP372−1, and doxorubicin (see Table 2), has also been shown to achieve their therapeutic effects through activation of FOXO3a and FOXO3a targets such as FasL, Bim, and p27.