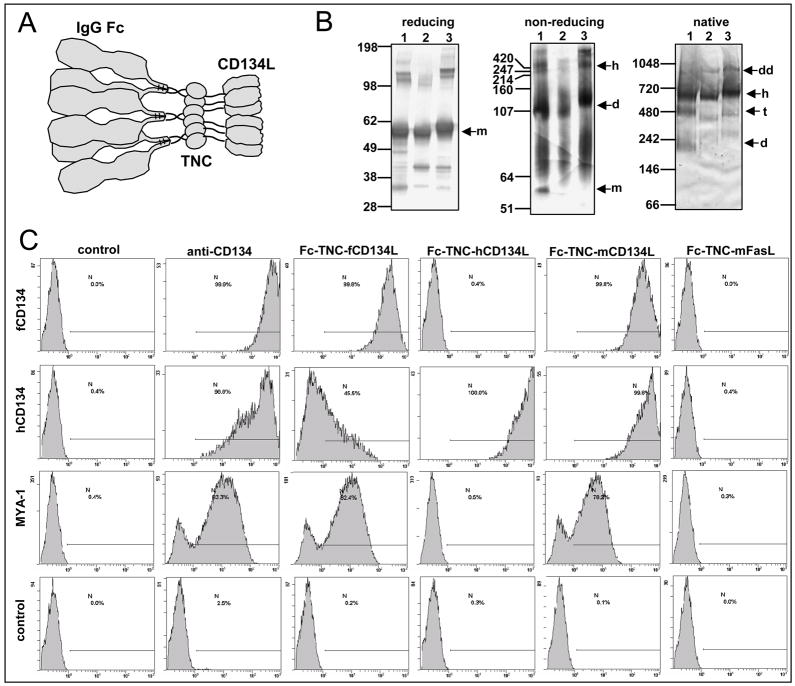
Fig. 2.
Enforced trimerisation of feline CD134L rescues ligand-specific binding. (A) Predicted hexameric structure of the Fc-TNC ligands, comprising three IgG Fc dimers and two CD134L trimers. (B) Polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analyses of the Fc-TNA-ligands on reducing SDS-PAGE, non-reducing SDS-PAGE or blue NativePAGE™. 1-Feline, 2-Murine, 3- Human; m-monomer, d-dimer, t-tetramer, h-hexamer, dd-dodecamer (C) Binding of Fc-TNC ligands to MCC cells expressing feline or human CD134 (or vector only control), or to MYA-1 cells. Fc-TNC-fCD134 was compared with Fc-TNC-mCD134, Fc-TNC-hCD134 or Fc-TNC-mFasL. Bound ligands were detected with phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated anti-IgG Fc. CD134 expression was assessed using mAb 7D6, bound antibody being detected with PE-anti-mouse IgG. Cells were processed for flow cytometry and histograms represent 10,000 events collected in LIST mode, bars illustrate percentage positive. Histograms are representative of two independent analyses.