Fig. 3.
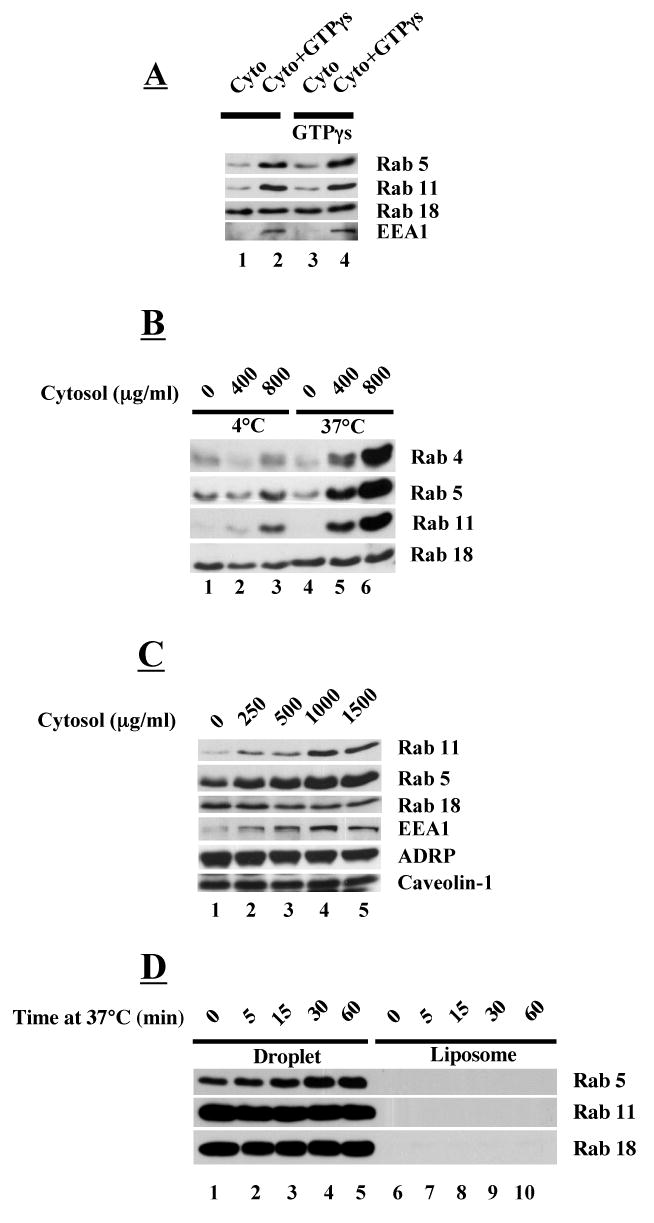
GTP-dependent recruitment of Rabs from cytosol to droplets (A-C) but not to liposomes (D). Rab proteins were released from droplets (A-C) with RabGDI as described in Figure 2. Droplets (50 μl, ∼20 μg protein/reaction) were mixed with either 80 μg of cytosol (A) or varying amounts of cytosol (B-C) in the presence or absence of 2 mM GTPγs. After incubation, droplets were washed three times and the proteins precipitated by acetone and processed for immunoblotting with an antibody against the indicated protein. A) GTPγs pre-bound to droplet is not sufficient to recruit Rabs and EEA1 to droplets. Droplets were either not treated (1,2) or pretreated with GTPγs and mixed with cytosol in the presence or absence of GTPγs at 37°C for 1 hr. B) Rab recruitment is dependent on temperature and cytosol concentration. Incubations were carried out at 4°C and 37°C with either 0, 400 μg/ml or 800 μg/ml of cytosol (volume 100 μl). C) Recruitment of Rabs and EEA1 appears to be saturable. Incubation was carried out at 37°C with the indicated concentration of cytosol (volume 100 μl). D) Rabs are not recruited to liposomes. Liposomes were prepared using lipids extracted from total CHO K2 cell membranes and mixed with 80 μg/ml of cytosol and incubated at 37°C for the indicated time. A companion set of droplets that had not been treated with RabGDI were processed the exact same way.
