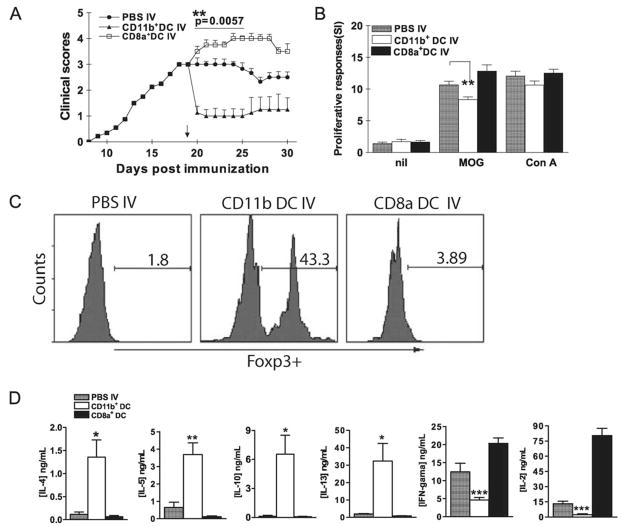
FIGURE 7.
Suppression of EAE by transfer of MOG-pulsed CD11c+CD11b+ DCs. A, Mice were sacrificed 3 wk after MOG35–55 i.v. tolerization. DCs were isolated from splenocytes using magnetic beads and separated into CD11c+CD11b+ and CD11c+CD8α+ DC subsets using a FACSAria. Sorted CD11c+CD11b+ and CD11c+CD8α+ DCs were i.v. transferred into EAE mice (5 × 105/mouse; n = 5 per group). Mice that received PBS-i.v. served as controls. Mean clinical EAE scores were determined on a daily basis. B, Seven days after transfer, splenocytes of DC-transferred or EAE control mice were isolated and cultured for 3 days with MOG35–55 (10 μg/ml), ConA (5 μg/ml) or without Ag/mitogen. Proliferative responses were measured by [3H]thymidine incorporation.**, p < 0.01. C, Cells isolated from spinal cords of mice described in A were stimulated with MOG35–55 (10 μg/ml) for 4 h, stained with Abs to CD4, CD25, and intracellularly Foxp3. CD4+CD25+ T cells were gated and Foxp3 expression of these cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. One representative experiment of three is shown. D, Seven days after transfer, splenocytes of DC- or PBS-transferred mice were isolated and cultured with MOG35–55 (10 μg/ml) for 3 days. Supernatants were harvested and cytokine production was assayed by ELISA. p values refer to comparisons between DC- or PBS-transferred mice.*, p < 0.05, ***, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001.