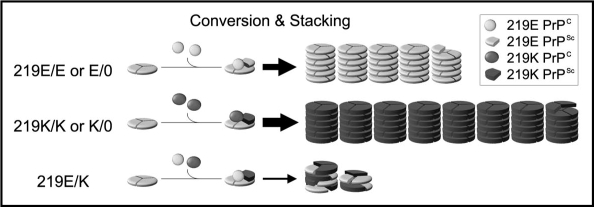
Figure 2.
The stone fence model: a possible mechanism of the heterozygous inhibition in vCJD infection. PrPC is converted to PrPSc and then piled up into amyloid fibrils according to the nucleated polymerization hypothesis and the trimeric models.25–28 In the homozygous (219E/E or K/K) or the hemizygous (219E/0 or K/0) animals, the PrPSc blocks are piled up into the amyloid fibrils without delay because only a uniform PrPSc population exists. Though the initial seed is 219E PrPSc also in the 219K/K or 219K/0 animals, the resulting 219K PrPSc acts as a new seed in the subsequent steps and are efficiently piled up. Therefore, the inhibitory effect of the initial 219E PrPSc seed is negligible in these animals. By contrast, in the heterozygous (219E/K) animals, at least two PrPSc populations are generated. These two PrPSc blocks are piled up into the same fibril just like a stone fence composed of heterologous blocks. The two types of PrPSc blocks interfere with each other due to their incompatible structures and delay the fibril elongation. Thus, the distinct PrPSc populations act as decelerators of each other in the heterozygous animals.