Figure 1. FcRn is required for IgG transport to fetus.
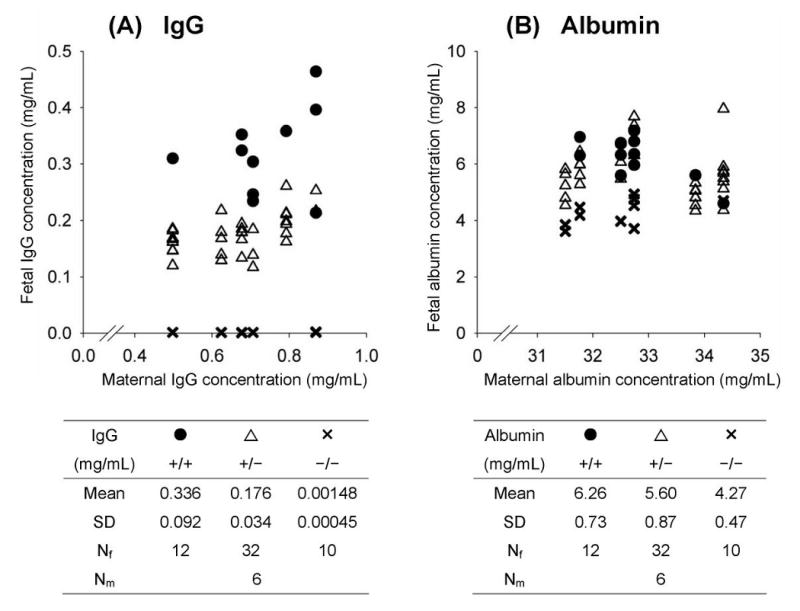
Serum concentrations, determined by ELISA, of IgG (Panel A) and albumin (Panel B) were normalized to transferrin levels to minimize inter-animal variation. Each point represents the fetal serum concentration of an individual pre-term fetus plotted against its maternal serum concentration. Mean values with SD and the number of fetuses in each strain (Nf) and mothers (Nm) are shown. Panel A: The mean fetal IgG concentration was significantly lower in FcRn−/− fetuses (✕) compared with both FcRn+/+ (●) and FcRn+/− (∆) fetuses. Also, the IgG level in FcRn+/− fetuses was about half that of FcRn+/+ fetuses. Panel B: Albumin concentrations of FcRn−/− fetuses were also significantly lower than in both FcRn+/− and FcRn+/+ strains.
