Figure 2.
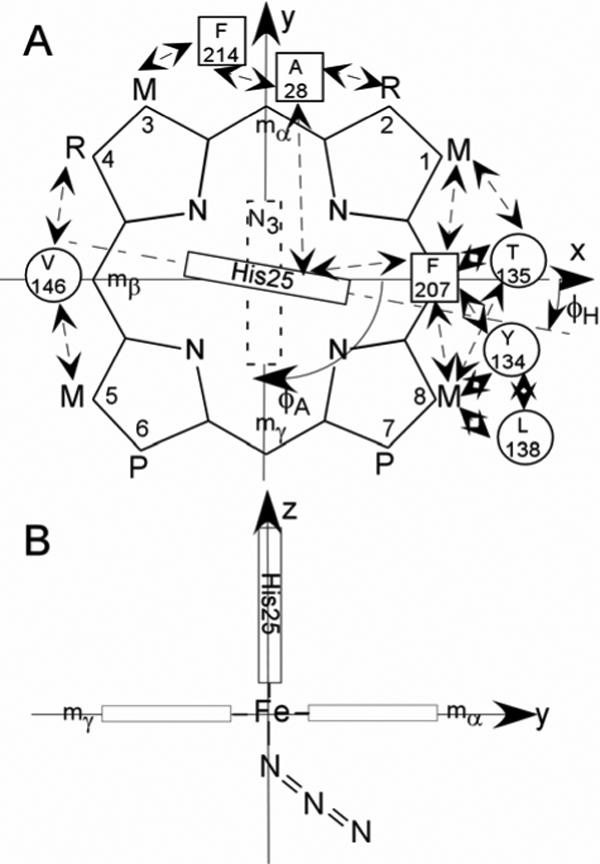
Structure of the (A) substrate, native protohemin, (PH; R = vinyl), and two-fold symmetric 2,4-dimethyldeuterohemin (DMDH; R = CH3). The coordinate system for the iron d orbitals has the x and y-axes passing through the β-,δ-meso positions (and His25 imidazole plane) and α-,γ-meso positions (azide π-plane), respectively, for the substrate orientation of the α-meso-selective hHO. The substrate contact residues are shown as squares and circles for proximal and distal residues, respectively. The orientations of the proximal His imidazole and distal azide π-planes are shown as solid and dashed rectangles, respectively; the angles between the x-axis and the proximal His imidazole and distal azide π-planes are φH and φA, respectively. Contacts expected from the crystal structures, (11, 13) and observed by 1H NMR for WT hHO-DMDH-N3, are shown by double-sided arrows; (B) edge-on view from the positive x-axis that depicts the expected Fe-N3 orientation, observed in the complex of rat HO. (62)
