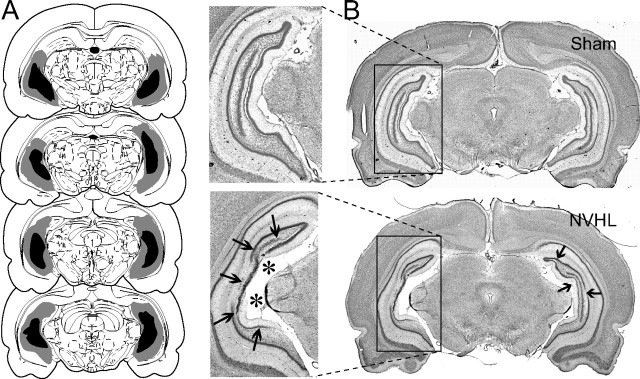
Figure 1.
Neonatal ventral hippocampal lesion. A, Drawings showing the extension of the ventral hippocampal damage induced by neonatal ibotenic acid observed in adulthood. Gray and dark areas indicate maximal and minimal extents of damage, respectively. B, Coronal Nissl-stained sections showing the ventral hippocampus of a sham rat (top, Sham) and a typical neonatal ventral hippocampal lesion (bottom, NVHL), characterized by cell loss (thick arrows) and enlarged ventricles (asterisks).