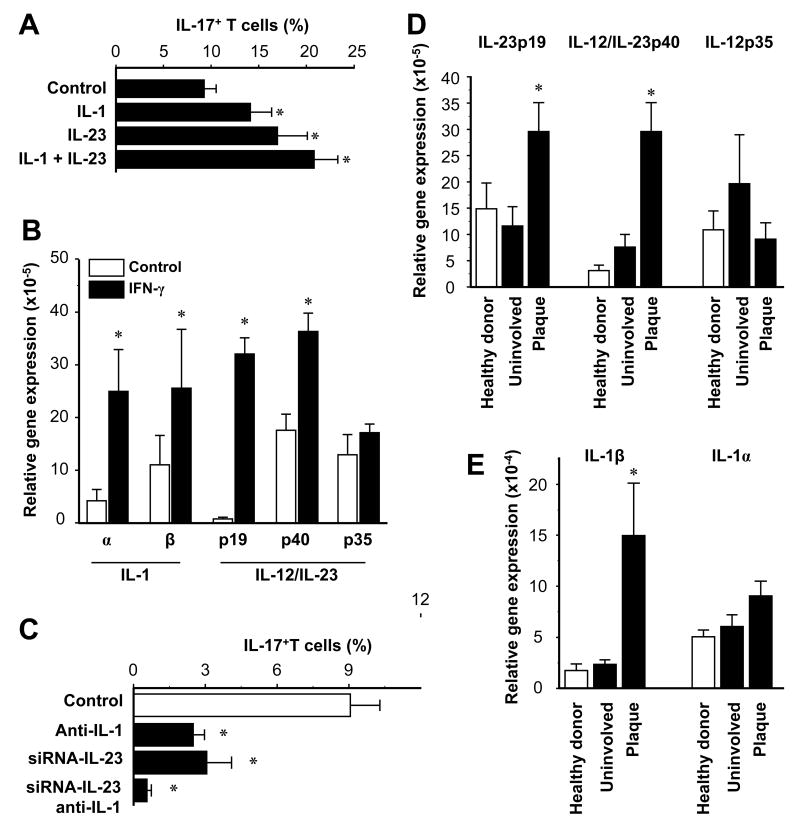
FIGURE 5.
Myeloid APCs stimulate IL-17+ T cell expansion through IL-1 and IL-23. A, IL-1 and IL-23 enhance the induction of IL-17+ T cells by CD11c+ cells. Normal peripheral blood T cells were stimulated for 5 days with normal CD11c+ myeloid APCs with or without IL-1 and IL-23 in the presence of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28. IL-17+ T cells were determined by FACS. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 7, * P < 0.03 compared to control. B, IFN-γ stimulates IL-1 and IL-23 expression by CD11c+ myeloid APCs. CD11c+ myeloid APCs were conditioned with or without IFN-γ. IL-1, IL-12 and IL-23 transcripts were quantified by QRT-PCR. Results are expressed as the mean of relative expression ± SEM, n = 7, *P < 0.01 compared to control. C, Blockade of IL-1 and IL-23 abrogates CD11c+ cell-mediated IL-17+ T cell induction. Blood-derived CD11c+ cells were transfected with IL-23-specific siRNA or control siRNA, then conditioned with IFN-γ. T cells were stimulated for 5 days with these myeloid APCs with or without neutralizing IL-1R antibodies. IL-17+ T cells were detected by FACS. Results are expressed as the mean of IL-17+ T cells in T cells ± SEM, n = 5, *P < 0.05 compared to control. D, E, Expression of IL-23, IL-12 and IL-1 were quantified by real-time PCR in skin from healthy donors and patients with psoriasis. Results are expressed as the mean of relative expression ± SEM, n = 5, *P < 0.03 compared to uninvolved and healthy skin.