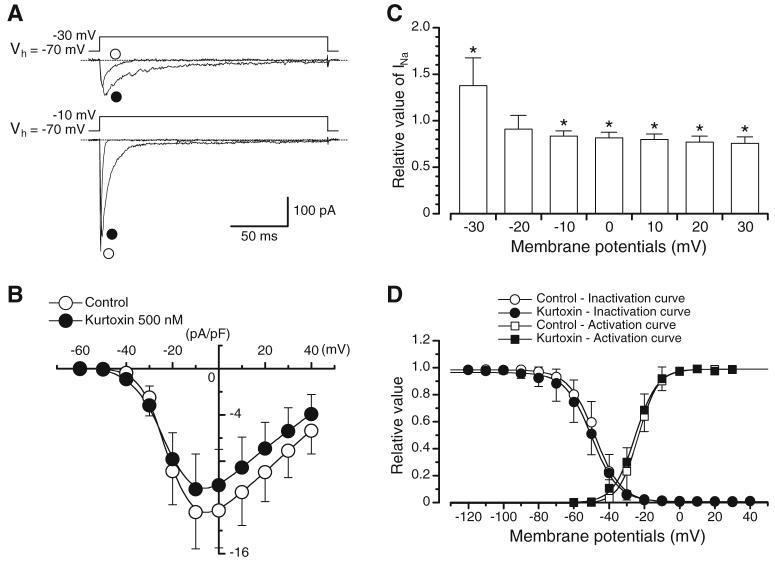
Fig. 1.
Actions of kurtoxin on INa. a Original current traces before and after application of kurtoxin at -30 and -10 mV. b Current-voltage relationships obtained in the absence or presence of kurtoxin. The current amplitude was measured as the peak amplitude of INa at each membrane potential. Each point indicates the current density (pA/pF), showing the mean+SD (n=7 cells, five different animals) shown by vertical lines. Some of the SD bars are less than the size of the symbol. c Relationship between the test potential and the relative value of INa in the presence of kurtoxin. The peak amplitude of INa evoked by depolarising pulses of various amplitudes in the absence of kurtoxin was normalised as one. Each column indicates the mean+SD (n=7 cells, five different animals) shown by vertical lines. Asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference demonstrated using a paired t test (P<0.05). d Effects of kurtoxin on the voltage-dependent activation and inactivation curves of INa. Steady-state inactivation curves, obtained in the absence and presence of kurtoxin, were fitted to the Boltzmann’s equation using the following values: control, Vhalf=-48.0 mV and k=7.5; kurtoxin, Vhalf=-49.8 mV and k=7.5. Each symbol indicates the mean+SD shown by vertical lines (n=7 cells, three different animals; P>0.05). Some of the SD bars are less than the size of the symbol. Activation curves in the absence and presence of kurtoxin, fitting to the Boltzmann’s equation using the following values: control, Vhalf=-23.5 mV and k=6.0; kurtoxin, Vhalf=-25.1 mV and k=6.0. Each symbol indicates the mean+SD shown by vertical lines (n=6 cells, four different animals; P>0.05)