Fig. 5.
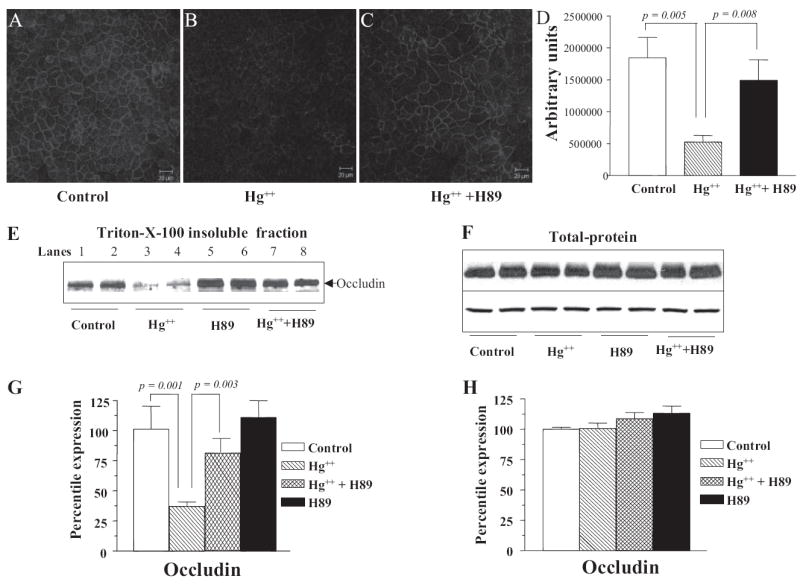
Addition of Hg2+ results in a decrease of occludin in the tight junctions via PKA-dependent mechanism. Confocal and Western blot analysis to determine occludin expression in the TJs of SMG-C6 cells: Cells were treated with PKA inhibitor H89 at time 0, and mercuric chloride was added after 60 min. Control (n = 3) (A), Hg2+ (n = 5) (B), and Hg2+ + H89 (n = 5) (C). D, fluorescence intensity was measured using ImageJ (National Institutes of Health). A minimum of seven fields were analyzed from each slide. E, Western blot of occludin in the tight junction fraction (Triton X-100-insoluble) of SMG-C6 cells. Equal loading in individual lanes was confirmed by staining the membrane with Ponceau S after transfer. F, Western blot of occludin in the total protein extracts of SMG-C6 cells. G, quantitation of the Western blots as shown in E from three individual experiments. H, quantitation of the Western blots as show in F from three individual experiments.
