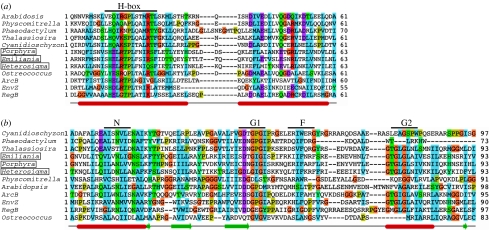
Figure 3.
Chloroplast sensor kinases show molecular evolution in their kinase domains. (a) Multiple sequence alignment of ycf26 and CSK HisKA domain (dimerization and phosphoacceptor domain as defined by SMART database) from representative species with the three canonical histidine kinases from bacteria, ArcB, EnvZ and RegB. Species names of ycf26 sequences are boxed. Predicted secondary structures are shown at the bottom. Alpha helices are shown as cylinders, beta sheets as thick arrows and the line connecting them as loops and turns. The site of autophosphorylation, H-box, located in the first helix of HisKA domain, is indicated on the top of the alignment. (b) The ATP-binding domain is conserved in all chloroplast sensor kinases. ATP-binding domain of representative ycf26, CSK sequences are aligned with those of three canonical histidine kinases, ArcB, RegB and EnvZ. Species names of ycf26 sequences are boxed. N, G1, F and G2 motifs of the ATP-binding domain are shown on top and the predicted secondary structures are shown at the bottom. Alignment was generated with ClustalW (Chenna et al. 2003) and edited with Jalview (Clamp et al. 2004). Secondary structures are predicted with JNet (Cole et al. 2008).