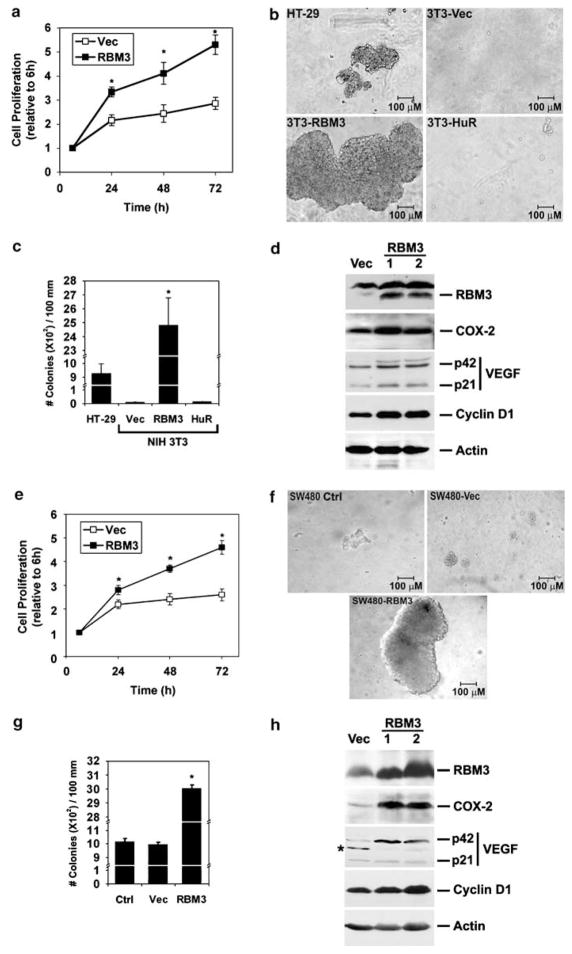
Figure 2.
RBM3 overexpression induces oncogenic transformation. (a) Proliferation of three independent NIH3T3-RBM3 clones were significantly higher than that observed with three independent NIH3T3-vector clones. (b) NIH3T3-RBM3 cells develop large colonies in soft agar, which are bigger than those formed by HT-29 cells. HuR overexpressing cells, on the other hand did not form any colonies in the soft agar. (c) Quantitative estimation of number of colonies formed in soft agar (*P<0.01). (d) Two clones of NIH3T3 cells stably expressing RBM3 were selected based on western blot analyses. Expression of COX-2, VEGF (p21 monomer and p42 dimer) and cyclin D1 increases in the RBM3 overexpressing cells. Clone 1 is the same one shown in b. (e) Proliferation of the SW480-RBM3 clones was significantly higher than that observed with SW480-vector clones. (f) SW480-RBM3 cells develop large colonies in soft agar, when compared to control, untransfected or vector transfected cells. (g) Quantitative estimation of number of colonies formed in soft agar (*P<0.01). (h) Two clones of SW480 cells stably expressing RBM3 were selected based on western blot analyses. Expression of COX-2, VEGF and cyclin D1 increases in the RBM3 overexpressing cells. Clone 2 is the same one as shown in f. *Nonspecific band. COX, cyclooxygenase; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.