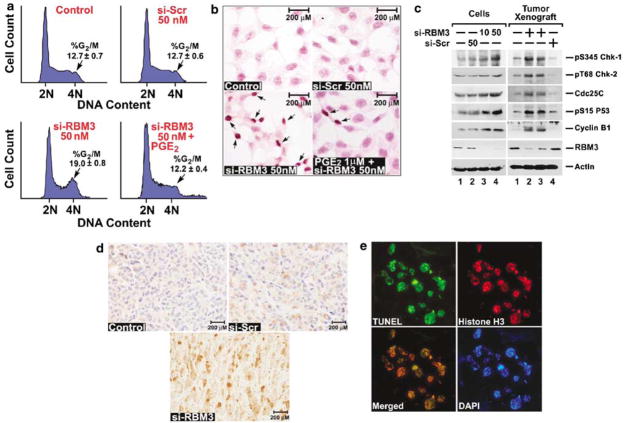
Figure 4.
RBM3 downregulation results in mitotic catastrophe. (a) siRNA downregulation of RBM3 increased cells in the G2/M phase. HCT116 cells were transfected at the indicated dose of either scrambled (si-Scr) or RBM3-specific (si-RBM3) siRNA for 72 h. Cell-cycle profiles were analysed by flow cytometry following PI staining for DNA content. The percentage of cells in the G2/M phase following si-RBM3 transfection was increased compared to control and si-Scr cells. Addition of PGE2 partially suppressed the RBM3 siRNA-mediated effects. (b) Knockdown of RBM3 leads to apoptosis. HCT116 cells following siRNA transfection were stained by the TUNEL method. Arrows show the TUNEL-positive cells, which were higher in si-RBM3 transfected cells, but less in cells also treated with 1 μM PGE2. (c) Loss of RBM3 induces checkpoint proteins. Lysates from HCT116 cells treated with si-Scr (50 nM) or si-RBM3 (10 and 50 nM), and tumor xenografts from the various treatments were subjected to western blot analyses using specific antibodies for phospho-Ser345 Chk-1, phospho-Thr68 Chk-2, Cdc25C, phospho-Ser15 p53 and cyclin B1. Actin was used as an internal control for loading the gels. (d) Lack of RBM3 increases cyclin B1 translocation to nucleus. Tumor xenografts were subjected to immunohistochemical staining for cyclin B1. The arrows in the si-RBM3 treated tumors indicate cyclin B1-positive cells in the nucleus. Representative photographs are a magnification of × 400. (e) RBM3 depletion leads to mitotic catastrophe. Tumors treated with si-RBM3 were stained for TUNEL (green) and phosphorylated histone H3 (red). The cells positive for both are shown in the merged image with yellow stain. DAPI is used to stain the nucleus. COX, cyclooxygenase; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; RT–PCR, reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction; siRNA, short interfering RNA; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.