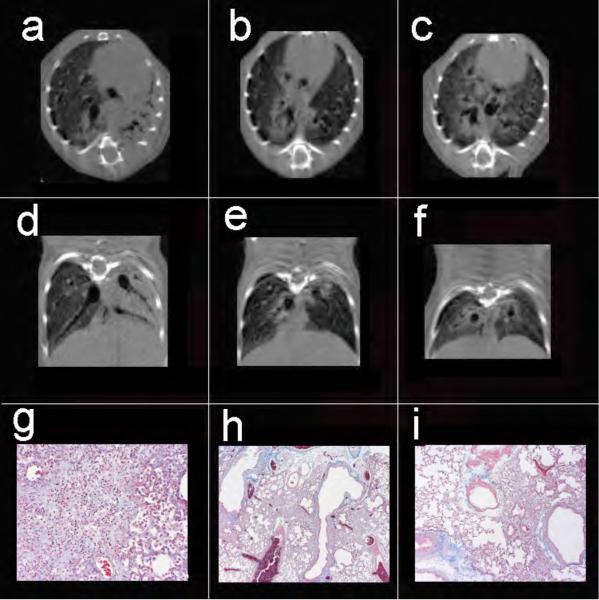
Figure 3.
Axial (a-c) and coronal (d-f) views of 3 mice exposed to 2.5, 3.0, and 3.5 U/kg bleomycin, respectively. Note the disparity in degree of injury with complete consolidation of the left lung, as well as peribronchial injury on the right in animal (a,d), focal peribronchial consolidation (b,e), and peribronchial as well as ground-glass injury (c,f). Despite the range of injury, Cqs measurements were 0.059, 0.056, and 0.056 ml/cm H2O respectively, while Cct in the same animals were 0.074, 0.074, and 0.056 ml/cm H2O respectively. Masson trichrome stains of the left lung from the three mice reveal diffuse confluent interstitial pneumonitis (g, 20x), peribronchial foci of interstitial pneumonitis with early fibrotic changes (h, 4x), and similar peribronchial fibrosis with adjacent normal lung (i, 20x).