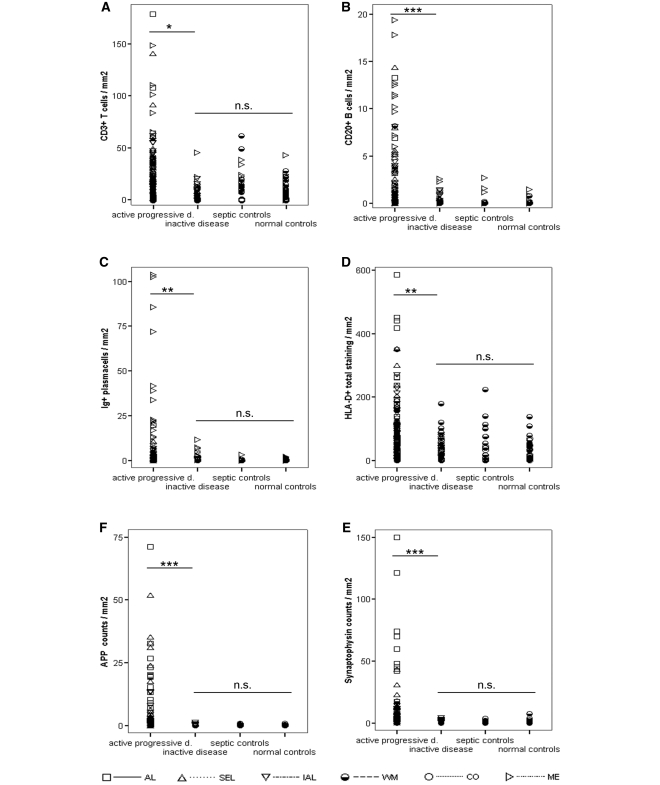
Figure 4.
The graph displays the differences between pathologically active progressive multiple sclerosis, pathologically inactive multiple sclerosis and controls (normal and septic controls). Among pooled progressive multiple sclerosis (SPMS and PPMS) patients, we have identified two distinct pathological subgroups: Pathologically active progressive multiple sclerosis cases had active lesions or slowly expanding lesions in white matter or cortex. Pathologically inactive multiple sclerosis cases only had inactive lesions in white matter and cortex. Apart from significant differences in their clinical presentation (Table 1), those entities also differ in their pathological presentation. Overall, pathologically active progressive disease cases display significantly higher densities of inflammatory infiltrates (A–D) and axonal injury (E and F) than pathologically inactive disease cases. Importantly, these differences remained when analysing inactive lesions or NAWM only (see Supplementary Table 3). In addition, pathologically active progressive disease cases also display significantly higher densities of inflammatory infiltrates (A–D) and axonal injury (E and F) than pooled controls. These differences were consistent using pooled data or values from either inactive lesions or NAWM only (the latter two not shown). Remarkably, even when using pooled data, both inflammatory infiltrates (A, C and D) and axonal injury (E and F) of pathologically inactive disease cases were in the range of normal or pooled control values. Areas of confounding pathology are not included. Multiple sclerosis values are lesional, normal appearing white matter, cortical and meningeal densities of inflammatory infiltrates (A–D) and lesional, NAWM and cortical densities of axonal injury (E and F). Control values are white matter, cortical and meningeal densities of inflammatory infiltrates (A–D) and white matter and cortical densities of axonal injury (E and F). Differences between pathologically active progressive, pathologically inactive disease and pooled controls have been assessed with Mann–Whitney U-tests by pooling all values (lesional, white matter, cortical and meningeal values). P-values are corrected with Shaffer's procedure. AL = active lesions; SEL = slowly expanding lesions; IAL = inactive lesions; WM, white matter; CO, cortex; ME, meninges; NS = not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.