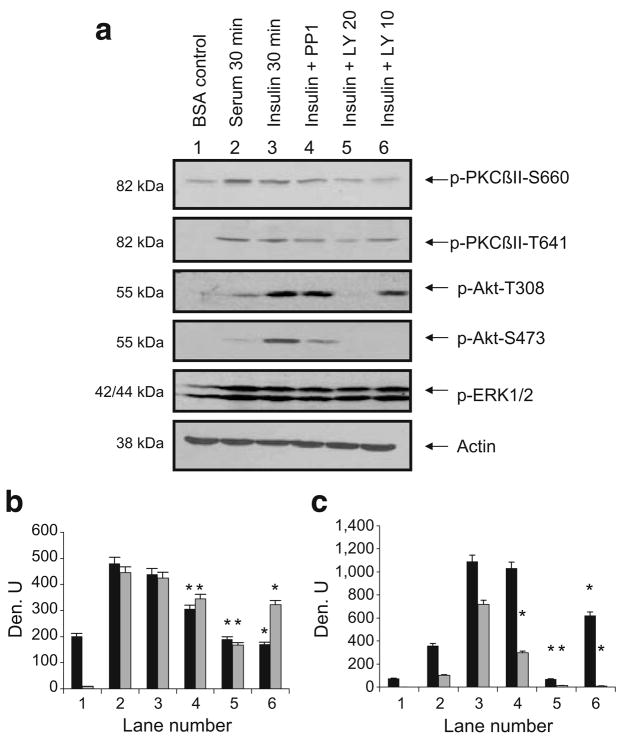
Fig. 1.
a Insulin increased phosphoPKCβII. L6 myotubes were serum-starved for 6 h prior to pretreatment with PP1 (10 μmol/l), LY294002 (20 or 10 μmol/l) for 30 min followed by serum (10%) or insulin (10 μIU/ml) for 30 min. Whole-cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE (10%) and transferred to membranes for western blot analysis as indicated with anti-phosphoPKCβII, phosphoAkt, phosphoERK1/2 or actin. Blots were scanned and quantitated using UnScanIt gel digitising software (Silk Scientific, Orem, UT, USA). b, c Relative densitometric units (Den. U) for phosphoPKCβII S660 and T641 and for phosphoAkt T308 and S473. Black bars show units for pPKCβII-S660 (b) and pAkt-T308 (c) and grey bars show units for p-PKCβII-T641 (b) and pAkt-S473 (c). The experiment was repeated three times. Significant inhibition (*p<0.05) of insulin effects by inhibitors on pPKCβII and pAkt sites, as determined using Prism4 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA) by one-way ANOVA. p, phospho