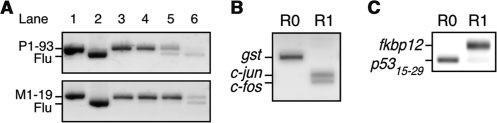
Figure 4.
The mRNA display selection of protein interactions on the Biacore sensor chip. (A) The P1-93 (912 bp; lane 1 top) or M1-19 (936 bp; lane 1 bottom) gene was mixed with an anti-fluorescein scFv gene (5) (Flu; 888 bp; lane 2) at a ratio of 1:102 (lane 3), 1:104 (lane 4), 1:106 (lane 5) or 1:108 (lane 6). The mixtures were subjected to mRNA display selection on the sensor chip conjugated with antigens p53 (top) or MDM2 (bottom). The RT-PCR products amplified from fractions after one round of selection were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. (B) In vitro selection of protein–DNA interactions was performed using a mixture of three genes with N-terminal T7·tag and C-terminal FLAG-tag coding sequences; c-fos (349 bp), c-jun (394 bp), gst (597 bp). The template RNAs of c-fos, c-jun and gst (negative control) were mixed at a ratio of 1:1:106. The mixtures were translated and the resulting mRNA-displayed protein libraries were selected on the sensor chip conjugated with bait DNA (AP-1) (14). The RT-PCR products amplified from fractions before (R0) or after one round (R1) of selection were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. (C) In vitro selection of protein–drug interactions was performed using a mixture of two genes with N-terminal T7·tag and C-terminal FLAG-tag coding sequences; fkbp12 (448 bp) and a p53 (15–29 aa) fragment (175 bp). The template RNAs of fkbp12 and the p53 fragment (negative control) were mixed at a ratio of 1:106. The mixtures were translated and the resulting mRNA-displayed protein libraries were selected on the sensor chip conjugated with bait drug (FK506) (15). The RT-PCR products amplified from fractions before (R0) or after one round (R1) of selection were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis.