Figure 5.
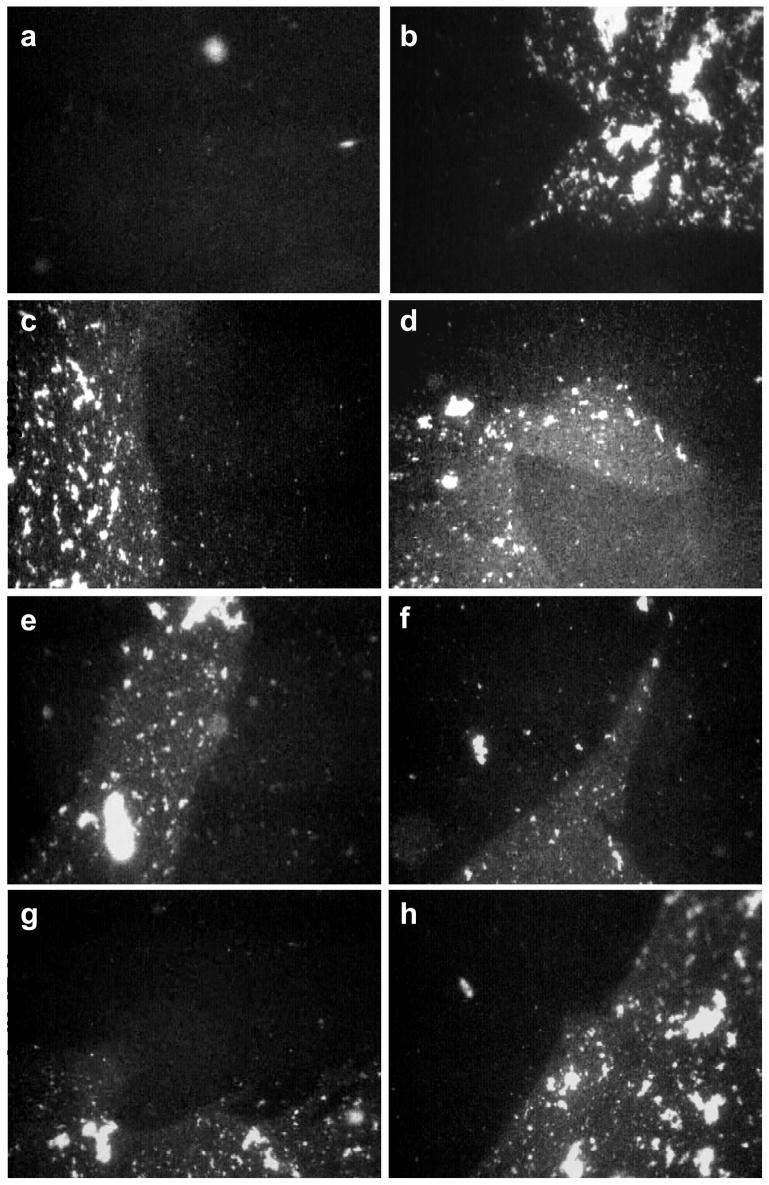
Fluorescence images of 800 μg Survanta spread on a saline buffered subphase containing 2 mg/mL albumin and 0.5 mg/mL chitosan. Images are 1023 μm by 789 μm.
First Cycle (a) Π = 25 mN/m during compression. The black homogenous background dominates the interface as the albumin prevents the Survanta from spreading as a monolayer. (b) Π = 18 mN/m during expansion. Survanta breaks through the interface; extended (>1000 μm) immiscible Survanta (mottled gray) and albumin (black) domains coexist on the interface.
Second Cycle (c) Π = 21 mN/m during compression. (d) Π = 18 mN/m during expansion. The albumin and Survanta domains coexist during the compression and expansion cycle.
Third Cycle (e) Π = 21 mN/m during compression. (f) Π = 18 mN/m during expansion. Albumin and Survanta domains coexist on the interface.
Fourth Cycle (g) Π = 24 mN/m during compression. (h) Π = 18 mN/m during expansion. Albumin remains on the interface through the fourth compression and expansion cycle. Apparently a sufficient quantity of Survanta does not adsorb to completely expel the albumin from the interface.
