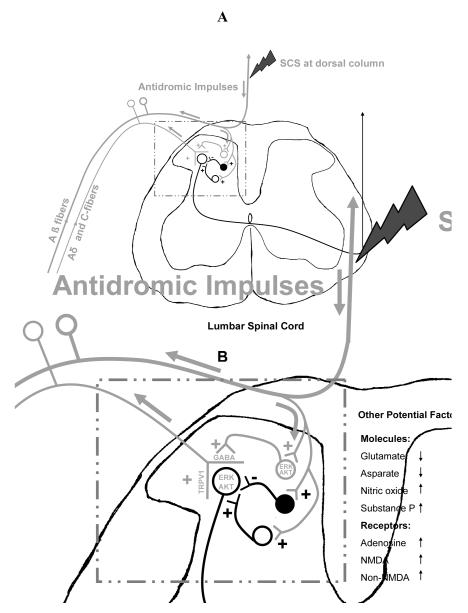
Figure 3. Potential mechanism how SCS activates central terminals of sensory fibers.
(A) Potential pathways. SCS at dorsal column antidromically activates large fibers, mainly Aβ fibers. A branch of Aβ fibers that connects spinal neurons in the superficial laminae of dorsal horn is also activated. Since these spinal neurons also presynaptically contact the central terminals of primary sensory fibers, activation of these spinal neurons subsequently produces primary afferent depolarization and further activate the central terminals of sensory fibers. (B) Potential factors. Based on the present study, ERK and AKT that localize in spinal neurons and central terminals of sensory fibers are involved in the activation of central terminals of sensory fibers produced by SCS at dorsal column. Other literature suggests that TRPV1 at the central terminals of sensory fibers is also activated.