Fig. 8.
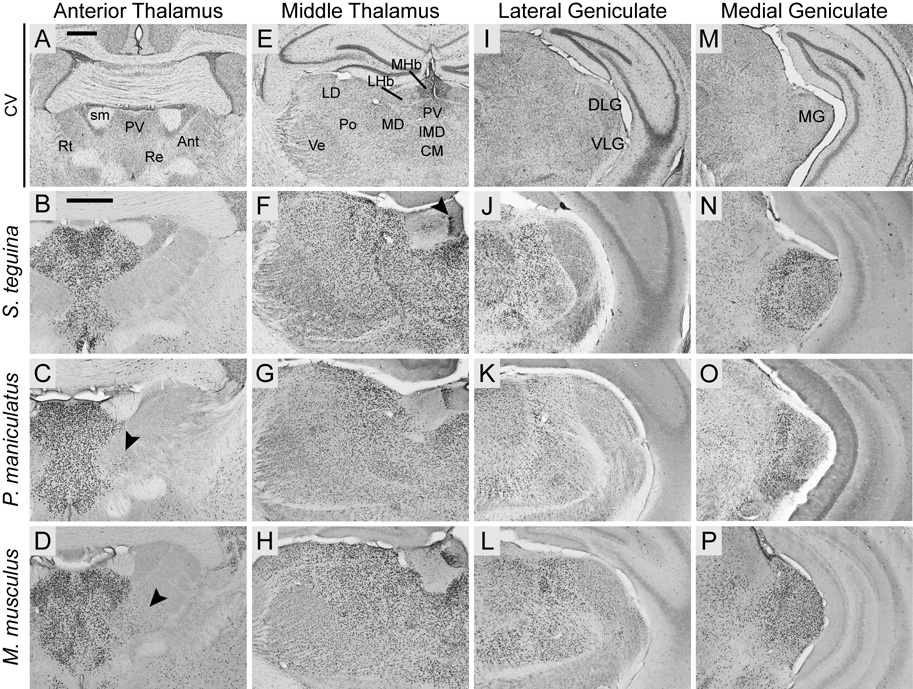
Foxp2 is widely expressed throughout the thalamus in Scotinomys (represented by S. teguina), P. maniculatus and M. musculus. A, E, I andM are coronal cresyl violet (CV) sections from S. teguina from approximately the same levels as representative examples of Foxp2 expression in B–D, F–H, J–L and N–P, respectively. B–D: Foxp2 is concentrated in midline and intralaminar nuclei, including paraventricular (PV) and reuniens (Re), and absent from reticular nucleus (Rt). Expression in anterior nuclei (Ant) is observed only in the anteromedial nucleus in P. maniculatus (arrow in C) and M. musculus (arrow in D). F–H: Uninterrupted expression in PV, intermediodorsal (IMD), central medial (CM), mediodorsal (MD), posterior (Po), laterodorsal (LD) and ventral nuclei (Ve), strong localized expression in the medial habenular nucleus (MHb; arrow in F), and diffuse expression in the lateral nucleus (LHb). J–L: Expression in lateral geniculate is concentrated in dorsal (DLG) relative to ventral (VLG) nuclei. N–P: Foxp2 is highly enriched in medial geniculate (MG). Scale bars = 500 µm in A (applies to A, E, I, M); 500 µm in B (applies to B–D, F–H, J–L, N–P); sm, stria medullaris of thalamus.