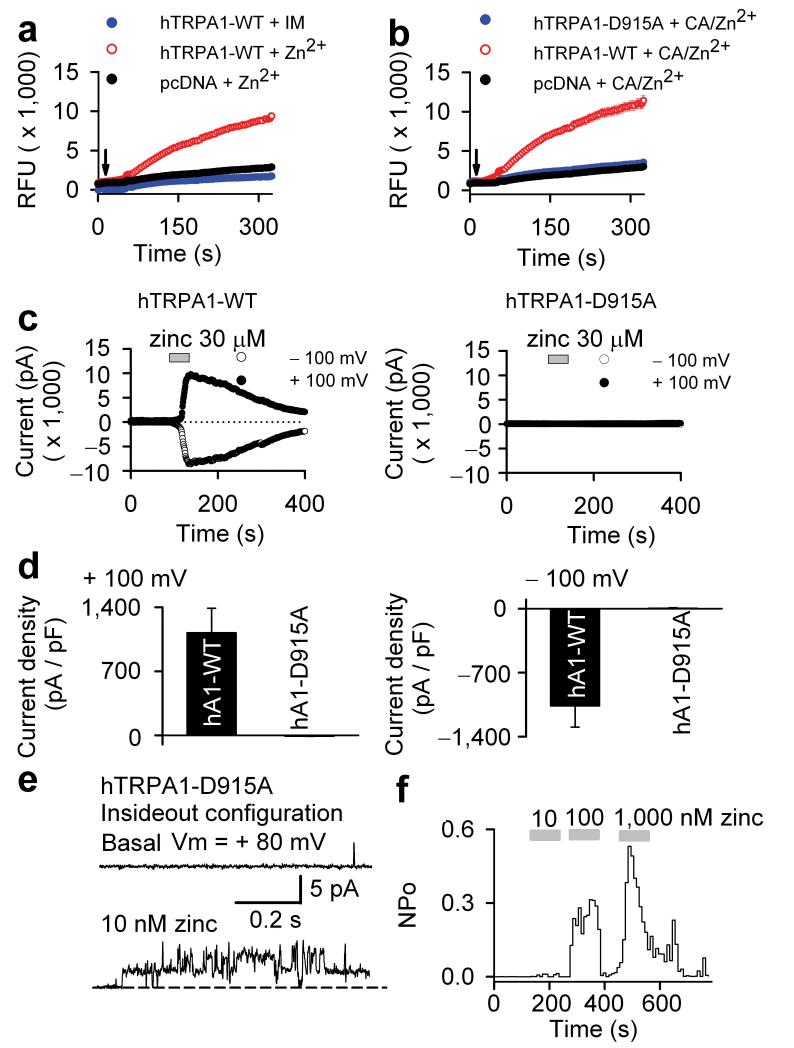
Figure 4. Zinc permeation through TRPA1 is required for activation by extracellular zinc.
(a) Zinc imaging (Fluozin-3) of wt TRPA1-transfected cells exposed to 30 μM ZnCl2 (red trace) or 2 μM ionomycin (IM, blue trace) at the indicated time (arrow). Vector control-transfected cells were exposed to 30 μM ZnCl2 (black trace). (b) Zinc imaging of cells transfected with wt TRPA1 (red trace), D915A mutant (blue trace) and vector control (black trace). Cells were exposed to 30 μM ZnCl2 in combination with cinnamaldehyde (CA, 1 mM) at indicted time (arrow). (c) Time course of zinc (30 μM)-activated whole-cell currents taken at +100 mV or -100 mV membrane potential in HEK293 cells transfected with wild type TRPA1 or TRPA1-D915A mutant. (d) 30 μM zinc-induced whole-cell current densities at +100 and -100 mV of HEK293 cells transfected with wild type TRPA1 and TRPA1-D915A mutant clones (n = 8 for wild type and n = 7 for TRPA1-D915A mutant). (e) Zinc increased single channel opening in an inside out patch excised from a HEK293 cell transfected with TRPA1-D915A (n = 7). Single channel traces are taken at +80 mV. (f) Histogram illustrates concentration dependent activation of single channels in an excised inside out patch from a TRPA1-D915A mutant expressing HEK293 cell.