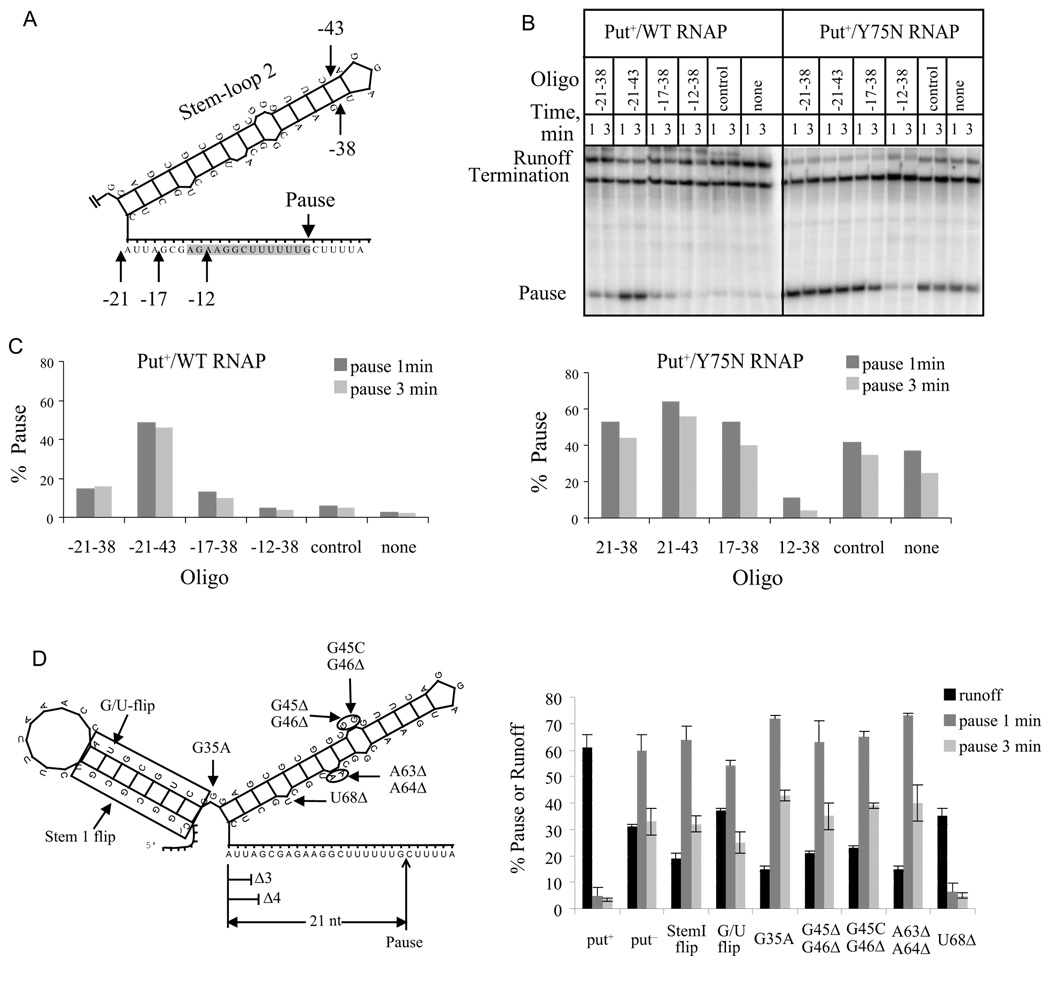
Fig. 6.
Effect of antisense oligonucleotide and putL mutations on pausing. The templates contained the PL promoter followed by WT or mutant putL sites followed by the U-rich pause followed by the TR′ terminator. A. The location of the 5' (-21, -17, and -12) and 3' (-43 and -38) ends of the antisense oligos are shown on stem-loop 2 of putL RNA. The numbers show position relative to G93. Stem-loop 1 is not shown, but is present in the templates of panels B and C. B. Transcription reactions were carried out using WT or Y75N RNAP in the absence or presence of the indicated oligonucleotide (100 µM). C. The fraction of paused transcripts obtained with WT (left) or Y75N RNAPs (right). The larger effect of oligo -21–43 compared to oligo -21–38 is probably because the former hybridizes more rapidly to putL RNA. D. (Left) A diagram of folded putL RNA showing mutations used in this experiment and that of Fig. 7A. (Right) Transcription was performed with WT RNAP, and the fraction of paused and runoff ECs calculated.