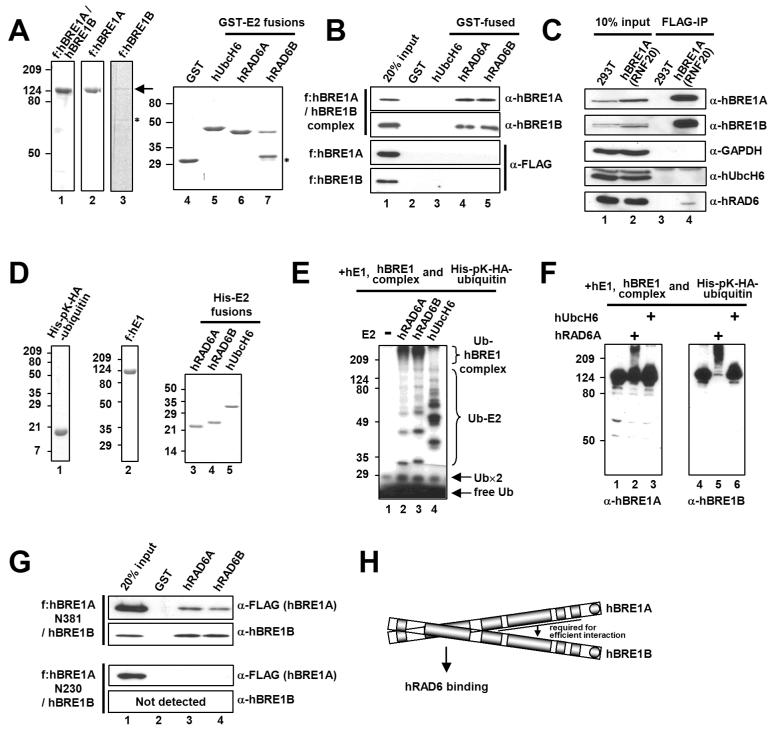
Figure 3. The hBRE1 Complex Directly and Specifically Interacts with hRAD6A and hRAD6B.
(A) Analyses of purified hBRE1 complex, FLAG-hBRE1A, FLAG-hBRE1B, GST and GST-E2 proteins by Coomassie blue staining. Asterisk, degradation product. (B) Selective binding of the hBRE1 complex to hRAD6A and hRAD6B. GST pull down assays employed the purified proteins shown in (A) and bound proteins were scored by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. (C) Intracellular binding of the hBRE1 complex to hRAD6. Total cell lysates from a FLAG-hBRE1A (RNF20) 293T cell line were incubated with M2 agarose, and bound proteins were visualized by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. (D) Analysis of purified His-pK-HA-ubiquitin, FLAG-hE1, and His-E2 proteins by Coomassie blue staining. (E and F) Ubiquitylation of the hBRE1 complex by hRAD6. The purified hBRE1 complex was analyzed in an E3 ubiquitylation assay with indicated E2 enzymes in the presence of either 32P-lablled (E) or unlabelled (F) ubiquitin, respectively, and ubiquitylation of the hBRE1 complex was monitored by autoradiography (E) or immunoblot (F), respectively. Ub×2 indicates a ubiquitin dimer. (G) Binding of the purified hBRE1 complex containing either FLAG-hBRE1A N381 or N230 fragments (Figure 1C) to hRAD6A and hRAD6B. (H) Schematic of direct binding of the hBRE1 complex to hRAD6.