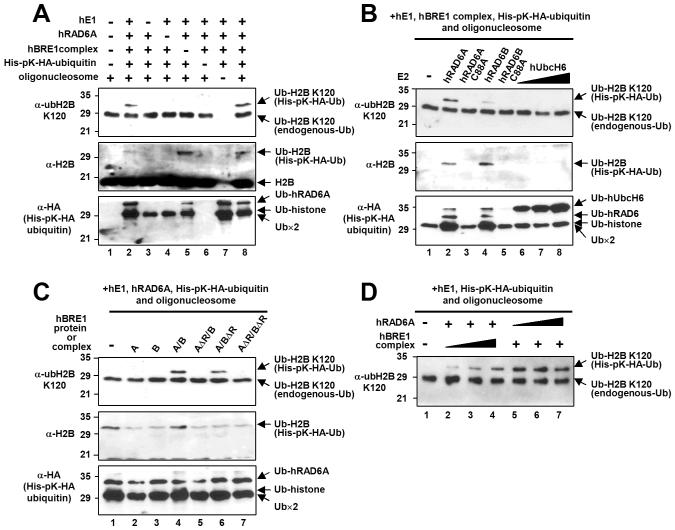
Figure 4. RAD6 Is the E2 Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme for H2B Lysine 120 Ubiquitylation in Human Cells.
(A-D) In vitro chromatin ubiquitylation assays. Reactions containing 5 μg oligonucleosome, 100 ng hE1, 200 ng E2, 600 ng hBRE1 complex and 2.8 μg His-pK-HA-tagged ubiquitin, unless otherwise indicated, were subjected to immunoblot with antibodies indicated on the left of each panel. (A) Collective requirement of factors for H2B ubiquitylation. Note that endogenous ubiquitylated H2B (in the oligonucleosome substrate) is not detectable by anti-H2B antibody (middle panel). (B) Comparison of hRAD6 and hUbcH6 E2 activities for H2B ubiquitylation. Reactions contained 200 ng wild-type or mutant hRAD6 (lanes 2-5) and 100 ng (lane 6), 200 ng (lane 7) or 600 ng (lane 8) hUbcH6. (C) hBRE1 complex RING finger requirement for H2B ubiquitylation. FLAG-hBRE1A, FLAG-hBRE1B and hBRE1 complexes (isolated via FLAG-hBRE1A) with intact or deleted (either or both) RING fingers are indicated. (D) The hBRE1 complex is limiting for H2B ubiquitylation. Reactions contained 50 ng (lane 2), 150 ng (lane 3) or 450 ng (lane 4) hBRE1 complex and 50 ng (lane 5), 100 ng (lane 6) or 200 ng (lane 7) hRAD6A.