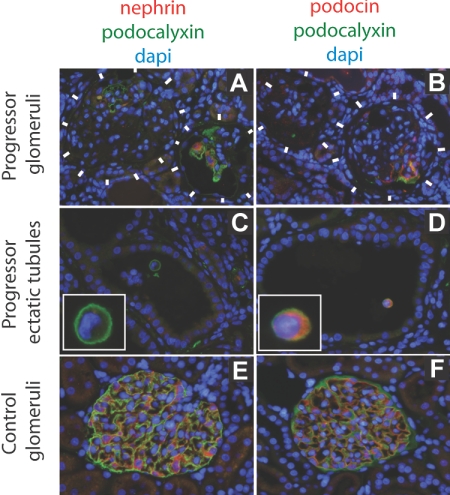
Figure 4.
Immunofluorescent photomicrographs developed for nephrin, podocin, and podocalyxin protein expression in progressor (chronic kidney disease) compared with normal kidney. The immunofluorescent color codes for each protein are shown above each set of panels. (A and B) Progressor (chronic kidney disease) rat glomeruli (delineated by white blocks) show absence of podocyte markers (podocalyxin, nephrin, or podocin) except in parts of glomeruli where intact podocytes still persisted in some glomeruli. (C and D) Podocytes in ectatic tubules in progressor renal cortex contain detached podocytes (identified by intense green podocalyxin immunofluorescent cell surface) that express podocin (D) but not nephrin (C). A higher magnification view of the detached podocytes is shown in the insets. (E and F) Normal glomerular podocytes express podocalyxin, nephrin, and podocin.