Figure 9.
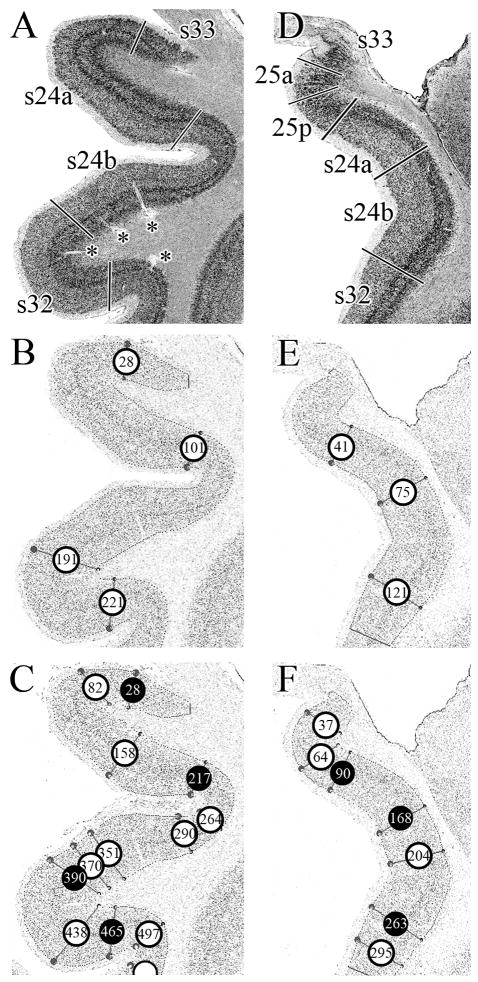
Assessment of areal borders with an algorithm-based quantification of the cortical laminar pattern. A. Cell-body, silver stained coronal section through a rostral level of sACC with areas 33, s24a, s24b and s32. B. GLI-image of the section shown in A, where darker pixels code for higher GLI values and lighter pixels code for lower values. The cortex was sampled with equidistant traverses from layer II to the layerVI/white matter boundary. Traverses were extracted every 6 pixels. The start and end points of the traverses are indicated by the dots in the image at these two boundaries, but the traverses have been removed to simplify the figure. The algorithm-based quantification of the cortical laminar pattern is insensitive to artefacts such as blood vessels (marked by asterisks in A). Circles indicate borders detected by the sliding window procedure at positions 28, 101, 191 and 221. C. GLI-image of the section shown in A, but traverses were extracted every 3 pixels (and not every 6 pixels, as in B). The sliding window procedure detected borders at positions 28, 82, 158, 217, 264, 290, 351, 370, 390, 438, 465, and 497. Black circles indicate the borders which coincide with the approach taken in B. D. Cell-body stained coronal section through a caudal level of sACC with areas 33, 25a, 25p, s24a, s24b, and s32. E. GLI-image of the section shown in D. Traverses were extracted every 6 pixels and the sliding window procedure detected borders at positions 41, 75 and 121. F. GLI-image of the section shown in A, but traverses were extracted every 3 pixels (and not every 6 pixels, as in E). The sliding window procedure detected borders at positions 37, 64, 90, 168, 204, 263, and 295. Black circles indicate the borders which coincide with the approach taken in E.