Figure 1.
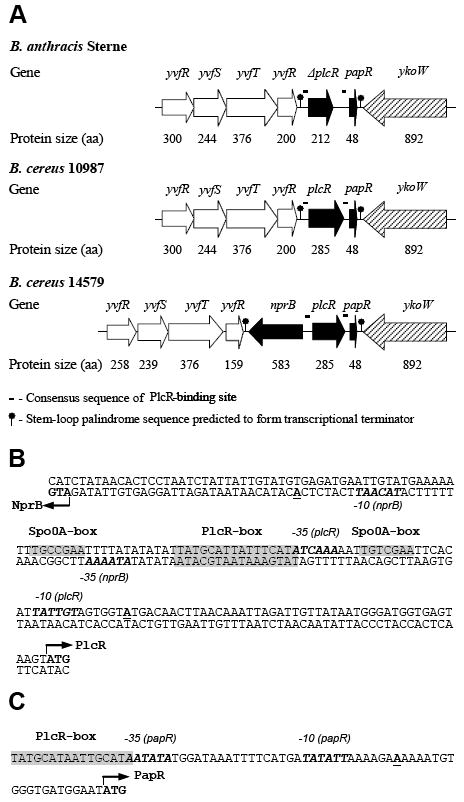
PlcR, PapR, and NprB genes. (A) B. anthracis Sterne, B. cereus 10987 and 14579 chromosomal DNA regions in the vicinity of plcR and papR genes. B. subtilis gene orthologues were selected by BLAST searches of the NCBI database: yvfR – ABC transporter (ATP-binding protein); yvfS – ABC transporter integral membrane protein; yvfT – two-component sensor histidine kinase; yvfU – two-component response regulator; nprB – neutral thermostable extracellular zinc metalloprotease; ykoW – protein, unknown function, likely to participate in prokaryotic signaling process. (B) Nucleotide sequence of B. cereus 569 nprB-plcR intergenic region. (C) Nucleotide sequence of B. cereus 569 papR promoter region. The predicted translation start codons for NprB, PlcR and PapR proteins are shown in bold type and indicated by arrows. Transcription start sites for all three genes (Okstad et al., 1999) are shown in bold type and underlined. The consensus binding sites for Spo0A and PlcR (Lereclus et al., 2000) are shaded. The putative – 10 and – 35 regions (Okstad et al., 1999; Agaisse et al., 1999) are indicated in italic and bold. All indicated sequences are the same for both B. cereus 569 and 14579 strains.
