Figure 2.
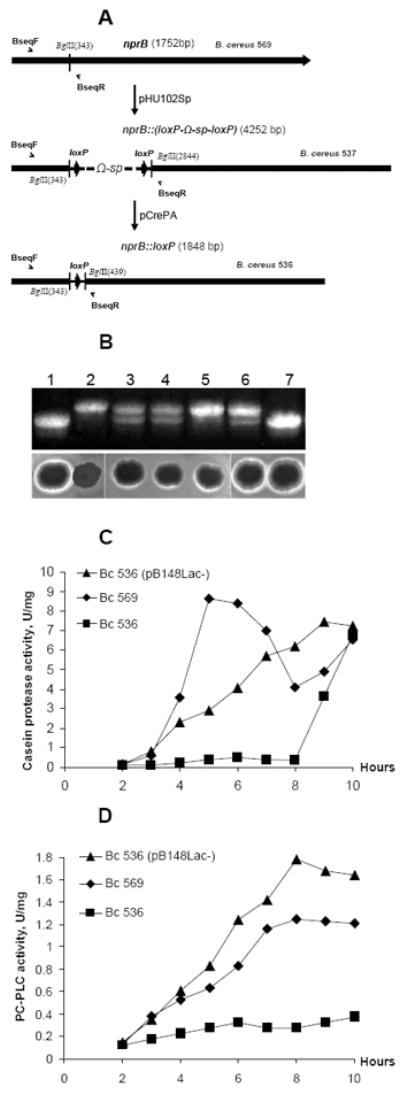
Inactivation of B. cereus 569 nprB gene. (A) Diagram of the genetic organization of the B. cereus 569 mutants, B. cereus 537 and B. cereus 536. Construction of the mutants is described in Materials and Methods. Arrows indicate the position and orientation of the loxP sites. Half-head arrows mark the position and orientation of the primers used for PCR analysis. (B) (Upper panel) The PCR fragments amplified with BseqF/BseqR primers from the chromosomal DNA of B. cereus 569 (lane 1), B. cereus 536 (lane 2), B. cereus 536 with plasmid pB148 (lane 3), B. cereus 536 with plasmid pB148Lac- (lane 4), B. cereus 536 with plasmid pFP12 (lane 5), B. cereus 536 with plasmid pHU102 integrated into chromosomal DNA as a single crossover event (lane 6), B. cereus 569 NprB-revertant obtained as a result of a double crossover event between pHU102 and B. cereus 536 chromosomal DNA (lane 7). Locations of the primers correspond to those shown in panel A. The upper fragment (398 bp) presents nprB-loxP allele; the lower fragment (302 bp) presents nprB allele. (Lower panel) Ability of B. cereus 569 to hydrolyze fresh blood is appreciably depressed in B. cereus 536. Transformation with pB148, pB148Lac-, pFP12 or pHU102 restored ability of B. cereus 536 to hydrolyze fresh blood. The locations of the samples correspond to those of the above PCR. (C and D) Casein proteolytic (C) and PC-PLC (D) activities of B. cereus 569, B. cereus 536, and B. cereus 536 (pB148Lac-) extracellular proteins. The strains were grown at 37°C in LB broth for 10 h with supernatant samples taken every hour. Equal amounts of extracellular protein (2-10 μg for PC- PLC and 10-50 μg for casein proteases analysis) were assayed either by the Red Amplex (PC- PLC) or green-fluorescent BODIPY FL (protease) reagents. Maximum root-mean-square deviations did not exceed 10% for the protease (C) and PC-PLC (D) determinations.
