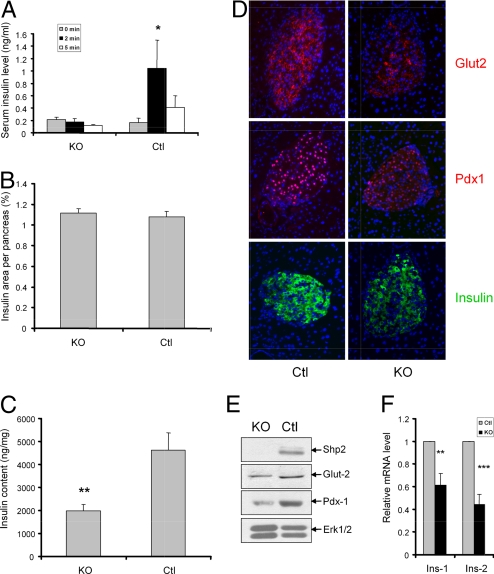
Fig. 2.
Shp2 ablation inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and insulin biosynthesis in β-cells. (A) Acute-phase insulin secretion after i.p. injection of glucose (3 g/kg of body weight) into 8-month-old Shp2Panc−/− and control mice (n = 7 for Shp2Panc−/− group; n = 4 for control group). All data are presented as means ± SEM. *, P < 0.05 (2-tailed student's t test). (B) Morphometric analysis of insulin-positive area of total pancreatic area from 3-month-old Shp2Panc−/− and control mice (n = 4 per group). (C) Islet insulin content (ng/mg of total protein) in 3-month-old Shp2Panc−/− and control mice (n = 5 per group, **, P < 0.01). (D) Immunofluorescence detection of Glut2, Pdx1, and insulin in pancreatic sections from Shp2Panc−/− and control mice. Blue staining, DAPI. (E) Immunoblot analysis of protein expression of Shp2, Glut2, Pdx1, and Erk in pancreatic islets isolated from Shp2Panc−/− and control mice. (F) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of Ins1 and Ins2 mRNA levels in isolated Shp2Panc−/− and control islets. **, P < 0.01 versus controls; ***, P < 0.001. All data are presented as means ± SEM.