Figure 6.
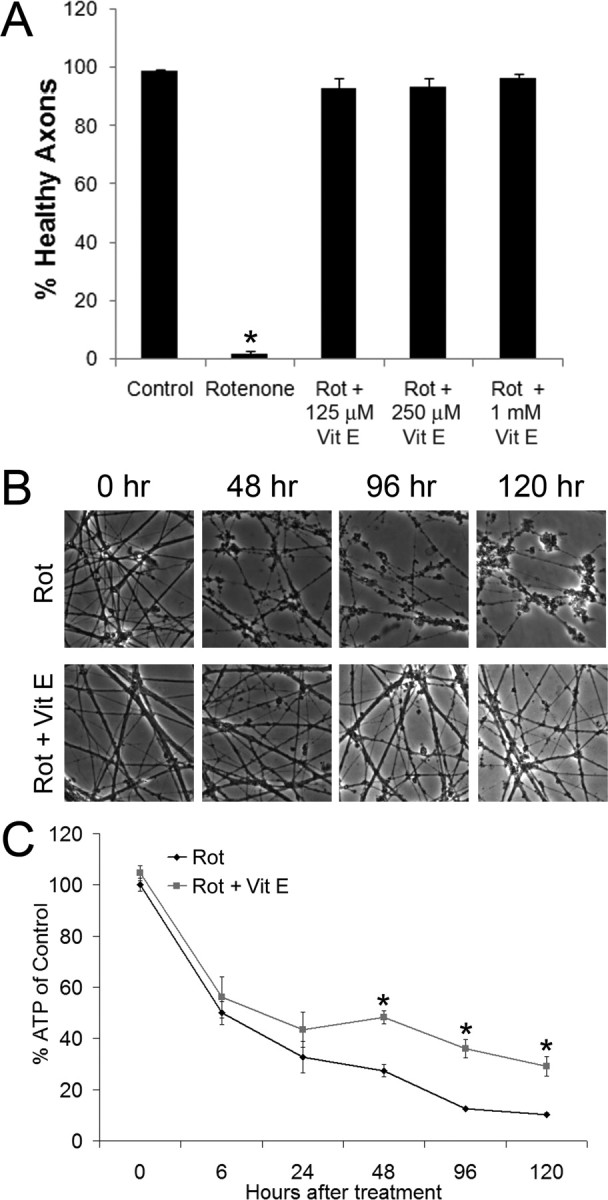
Vitamin E prevents axonal degeneration but does not affect initial ATP losses. A, DRG neurons were treated with rotenone (2.5 μm) and the indicated doses of vitamin E. Axonal degeneration was quantified after 6 d of treatment using images obtained by phase-contrast microscopy (*p < 0.05 compared with control; n = 6 wells per condition from duplicate experiments; error bars represent ±SEM). B, DRG neurons were treated with rotenone (2.5 μm) in the presence or absence of vitamin E (1 mm), and axonal degeneration was assessed by phase-contrast microscopy. Whereas axons in cultures treated with rotenone only were visibly damaged by 48 h, neurons treated with rotenone and vitamin E were intact at 120 h. C, DRG cultures were treated with rotenone (2.5 μm) in the presence or absence of vitamin E (1 mm), and ATP levels were measured at the indicated time points. Vitamin E failed to prevent the initial loss of ATP (*p < 0.05; n ≥ 6 wells from duplicate experiments; error bars represent ±SEM).
