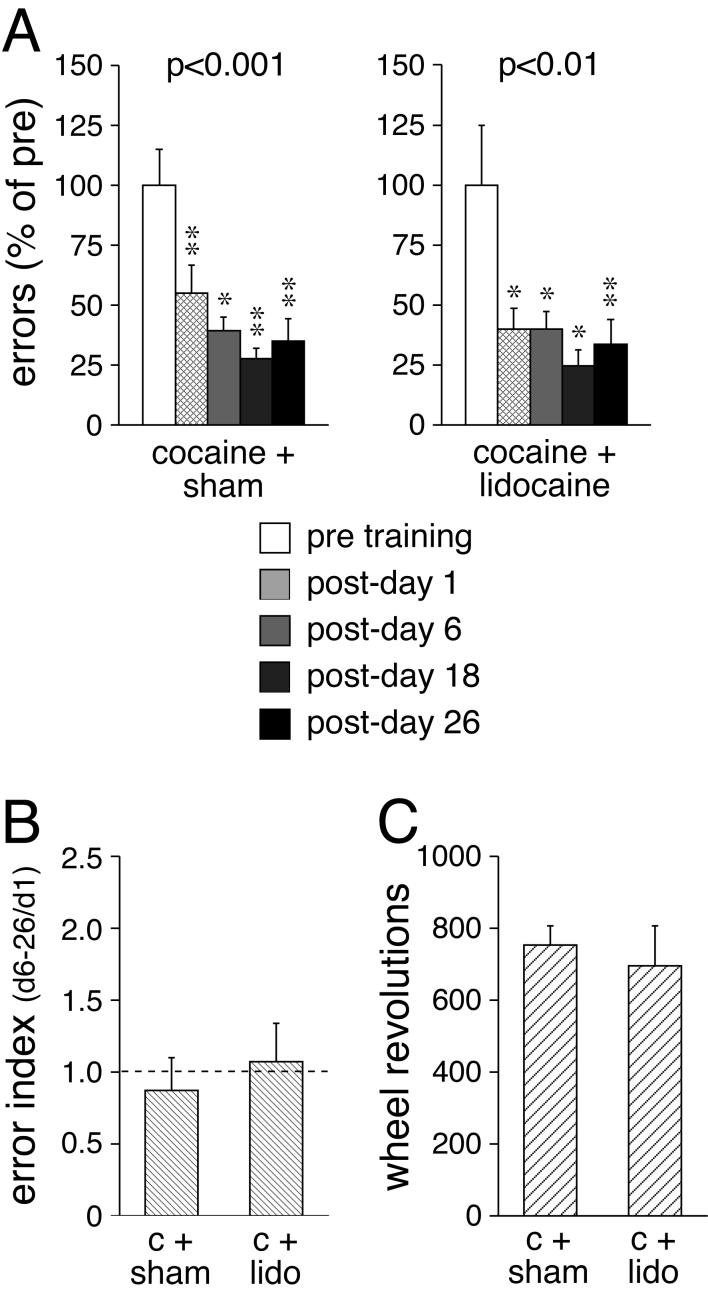
Fig. 3.
Effects of post-trial interference by lidocaine infusion into the striatum on motor-skill learning under the influence of cocaine. A The number (mean±SEM) of errors (in percent of pre-test values) committed before (pre) and 1, 6, 18 and 26 days after (post) the 2-day training is given for rats that received a bilateral intrastriatal infusion of lidocaine (2%, 1 μl each side) or a sham infusion after each training session. All rats received an injection of cocaine (25 mg/kg, i.p.) before each training session. The p value for the overall training effect is also shown. B The error index (averaged errors on post-days 6-26 divided by errors on post-day 1; mean±SEM) is shown for sham (c+sham)- and lidocaine (c+lido)-treated groups. C The total number (mean±SEM) of wheel revolutions during the training for these groups is depicted. ** p<0.01, * p<0.05 vs. pre.