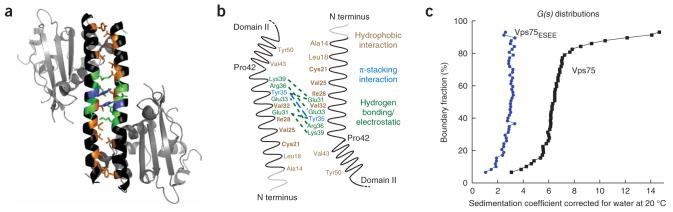
Figure 4.
Dimerization between domain I of Vps75 monomers. (a) Vps75 monomers interact with symmetry mates in adjacent asymmetric units creating a dimer through domain I helix (residues 8-53). Residues are colored to indicate those involved in forming the dimer interface and type of interaction with hydrophobic interactions in brown, hydrogen-bonding in green and π-stacking in blue. Domain II is shown in gray. (b) Cartoon of interaction surface created by domain I of Vps75. Residues are colored according to interaction type as in a. Gray sections are not resolved in the current structural models of Vps75. Residues labeled in bold are altered in the Vps75ESEE construct (containing C21E V25S I28E V32E substitutions). (c) Spectra from analytical ultracentrifugation of wild-type Vps75 (black squares) and Vps75ESEE (blue circles).