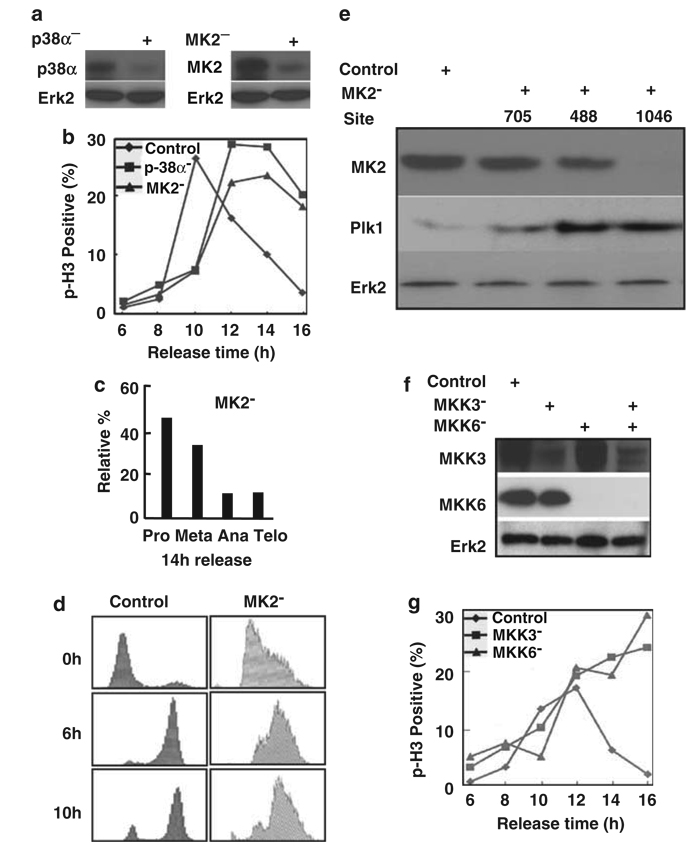
Figure 2.
The p38 MAP kinase pathway is required for mitotic progression. (a) HeLa cells were transfected with siRNA by targeting p38α (left panel), or targeting MK2 (right panel). Cells were harvested at 2 days post-transfection, and lysates were analysed by western blot. (b) Cells were depleted of p38α or MK2 as described in (a), subjected to the double thymidine block, released for different times and stained with a phospho-histone H3 (p-H3) antibody. (c) Relative percentages of different subphases of mitosis of MK2-depleted cells at 14 h post-release. (d) MK2 was depleted in synchronized cells as in (b). After release from thymidine block for different times as indicated, cells were harvested for fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis. (e) MK2 depletion leads to Plk1 stabilization. HeLa cells were transfected with pBS/U6-MK2 by targeting three different sites (nt 705, nt 488 and nt 1046). At 2 days post-transfection, cells were harvested and subjected to western blot using the antibodies indicated. (f) HeLa cells were transfected with siRNAs to deplete MKK3, MKK6 or MKK3/6. At 2 days post-transfection, cells were harvested and analysed by western blot. (g) HeLa cells were depleted of MKK3 or MKK6 as described in (f), subjected to the double thymidine block, released for different times and stained with a phospho-histone H3 (p-H3) antibody.