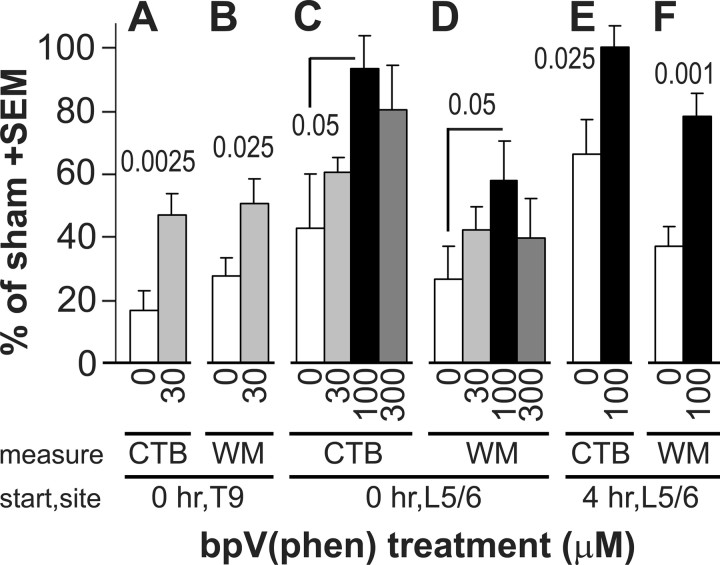
Figure 2.
PTP inhibition by bpV(phen) treatment rescues dorsal column sensory axons and white matter. The concentration of bpV(phen), the histological measure, the time after the spinal cord contusion when the treatment was started (start), and the infusion site (site) are indicated below the graph. A, After a 7 d infusion of 30 μm bpV(phen) at the T9 contusion site started immediately after the injury, more sensory axons remained intact than with PBS (0), as measured by the CTB-labeled terminal fiber area in the gracile nucleus. p values were less than the numbers above the bars. Values are expressed as a percentage of seven sham-operated rats. B, bpV(phen) also protected the dorsal column white matter (WM) at the injury epicenter. C, D, A dose–response study using 7 d infusions at L5/6 started immediately after the injury showed that 100 μm bpV(phen) was most effective in protecting gracile nucleus innervation (C, CTB) and T9 dorsal column white matter (D). E, F, When started 4 h after the contusion, 7 d L5/6 bpV(phen) infusions also rescued gracile nucleus innervation (E) and T9 dorsal column white matter (F).